| Name | Narrow Angle Glaucoma |
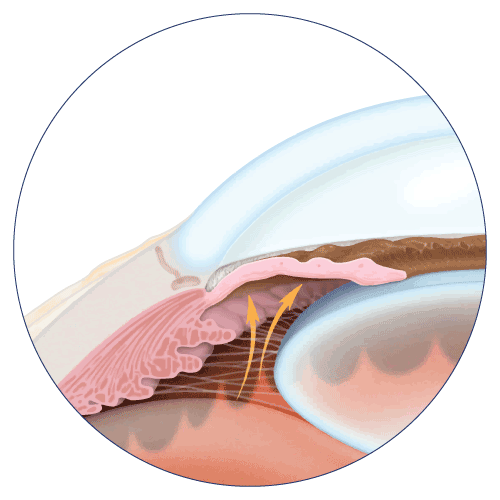
Narrow Angle Glaucoma
What is Narrow-angle glaucoma?
Narrow-angle glaucoma is a type of glaucoma characterized by a narrow-angle between the iris and the cornea, which can obstruct the flow of fluid in the eye and lead to increased pressure.
What are the causes of narrow-angle glaucoma?
Causes of narrow-angle glaucoma can include:
- Anatomic factors, such as a narrow iridocorneal angle or a large iris.
- The use of certain medications, such as miotics or antihistamines, can constrict the pupil and narrow the angle.
- Age-related changes in the eye, such as the natural contraction of the pupil or the progression of cataracts.
What are the symptoms of narrow-angle glaucoma?
Symptoms of narrow-angle glaucoma can include
- sudden severe headache
- eye pain
- nausea and vomiting
- blurred vision
- halos around lights
- eye redness
Treatment for narrow-angle glaucoma typically involves medications, such as topical beta-blockers or prostaglandin analogs, to lower eye pressure. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to open the angle and restore the normal flow of fluid in the eye.
Risk factors for narrow-angle glaucoma include
- a family history of the condition
- a history of farsightedness or nearsightedness
- the use of certain medications.
Prevention of narrow-angle glaucoma involves regular eye exams, especially for those at high risk, and avoiding the use of medications that can constrict the pupil and narrow the angle. If you have a family history of glaucoma or are at high risk for the condition, it is important to discuss any concerns with an eye doctor and to have regular eye exams to monitor eye pressure.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English