| Name | Perforation |
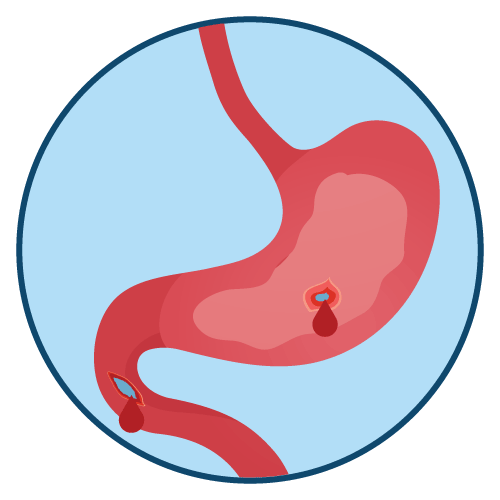
Perforation
Perforation is the formation of a hole or tear in a body organ or tissue. Perforation can occur in any organ or tissue of the body, but it most commonly occurs in the stomach, intestines, and eardrum.
Causes: Perforation can be caused by a variety of factors, including trauma, infection, inflammation, and medical procedures. For example, a perforated eardrum can be caused by a sudden change in pressure, such as during air travel or scuba diving. Perforation of the stomach or intestines can be caused by inflammation due to conditions such as Crohn's disease or Ulcerative colitis, or by a physical injury or surgical complication.
Symptoms: The symptoms of perforation vary depending on the location and severity of the perforation. Some common symptoms include:
- Abdominal Pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
- Chills
- Rapid heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Tenderness or swelling in the affected area
- Drainage from the ear (in the case of a perforated eardrum)
Treatment: Treatment for perforation depends on the location and severity of the perforation. In some cases, a small perforation may heal on its own with rest and antibiotics. In more severe cases, surgery may be required to repair the perforation and prevent further complications. Treatment may also include medication to manage pain and prevent infection.
Prevention: There are several steps you can take to prevent perforation, such as:
- Taking care to avoid physical injuries that could damage organs or tissues
- Managing any underlying conditions that increase the risk of perforation, such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis
- Following appropriate safety precautions during medical procedures, such as endoscopies or colonoscopies
- Avoiding exposure to loud noises or sudden changes in pressure that could cause a perforated eardrum.
In summary, perforation is the formation of a hole or tear in a body organ or tissue. It can be caused by a variety of factors, and the symptoms and treatment depend on the location and severity of the perforation. Taking steps to prevent perforation is important to maintain overall health and wellness.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English