Medicine details
| Image |  |
| Name | Premicon |
| Dosage | Tablet |
| Generic Name | Conjugated OEstrogen |
| Classes |
Dermatological/Topical Agent Vaginal Preparation |
| Diseases |
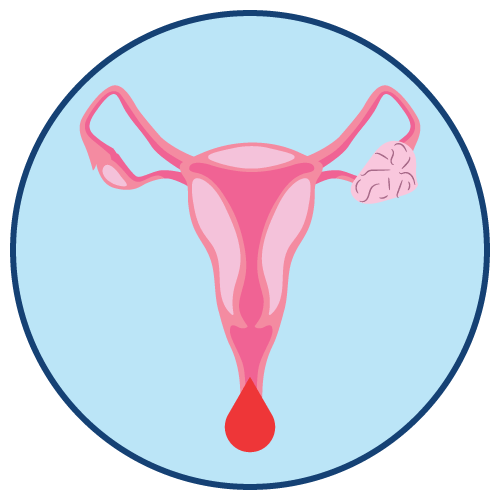
Abdominal Uterine Bleeding Hormonal Disorder Hypogonadism Osteoporosis (Brittle Bone) |
| Company | Techno Drugs Ltd. |
Drug Package Details
| Strength | 625 mcg |
| Storage Condition | |
| Origin Country | Bangladesh |
| Commercial Pack | 28 |
| Price per pack | ৳ 422.00 |
| Cost per pack | ৳ 371.36 |
| Package unit | 4 tabs strip |
| Price per unit | ৳ 15.07 |
| Cost per unit | ৳ 13.26 |
| Discount | 0 |
| Coupon | |
| Remarks |
Conjugated OEstrogen
Conjugated estrogens belong to the class of drugs known as hormone replacement therapy (HRT) agents. They are a mixture of estrogen hormones that are derived from the urine of pregnant mares. The mechanism of action of conjugated estrogens involves binding to estrogen receptors and modulating the expression of various genes, resulting in effects on reproductive tissues, bone, and other organs.
Conjugated estrogens are indicated for the following conditions:
- Treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause.
- Treatment of vulvar and vaginal atrophy, vaginal dryness associated with menopause.
- Prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis.
The recommended dosage of conjugated estrogens depends on the indication and the patient's individual response. The lowest effective dose should be used for the shortest duration possible to achieve treatment goals. The following are general guidelines:
- For the treatment of vasomotor symptoms and vulvar and vaginal atrophy: 0.3-1.25 mg daily, depending on the severity of symptoms.
- For the prevention of osteoporosis: 0.3-0.625 mg daily.
Adverse reactions to conjugated estrogens are common and may include the following, listed in order of decreasing frequency:
- Headache
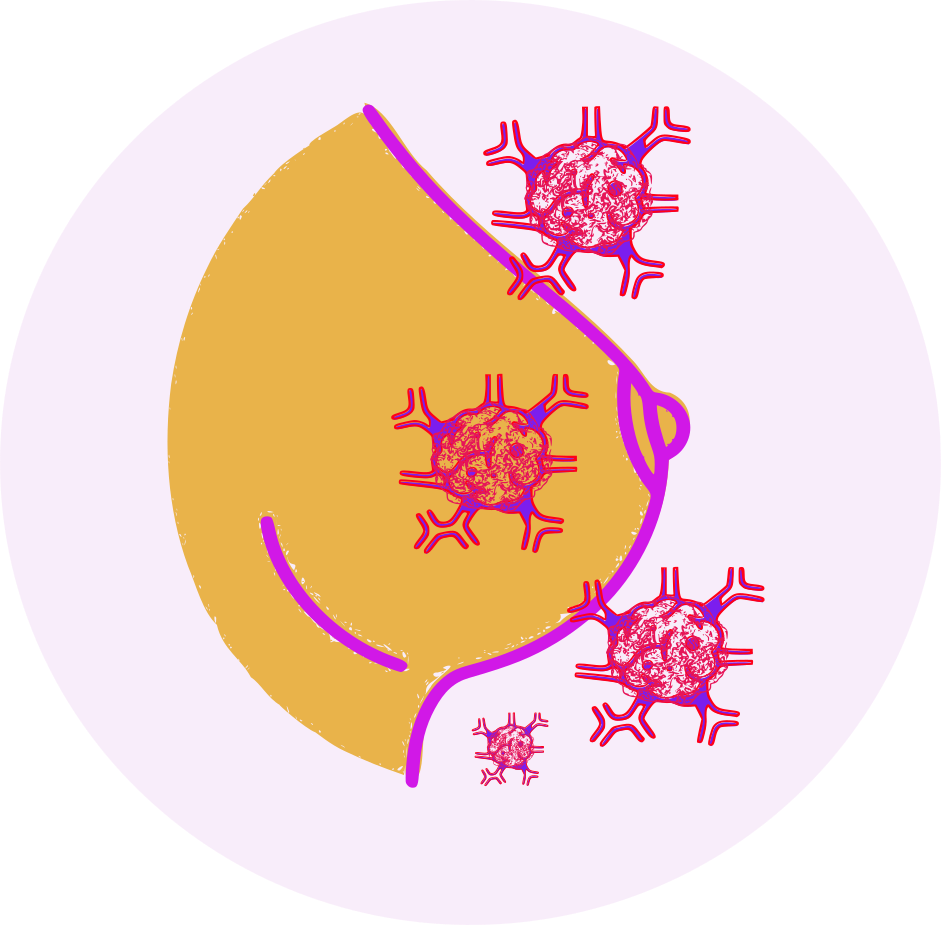
- Breast pain
- Irregular vaginal bleeding or spotting
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal cramps or bloating
- Fluid retention
- Elevated blood pressure
- Mood changes
- Estrogens increase the risk of endometrial cancer, especially in women with intact uteri. Progestins should be co-administered with conjugated estrogens in women with intact uteri to reduce this risk.
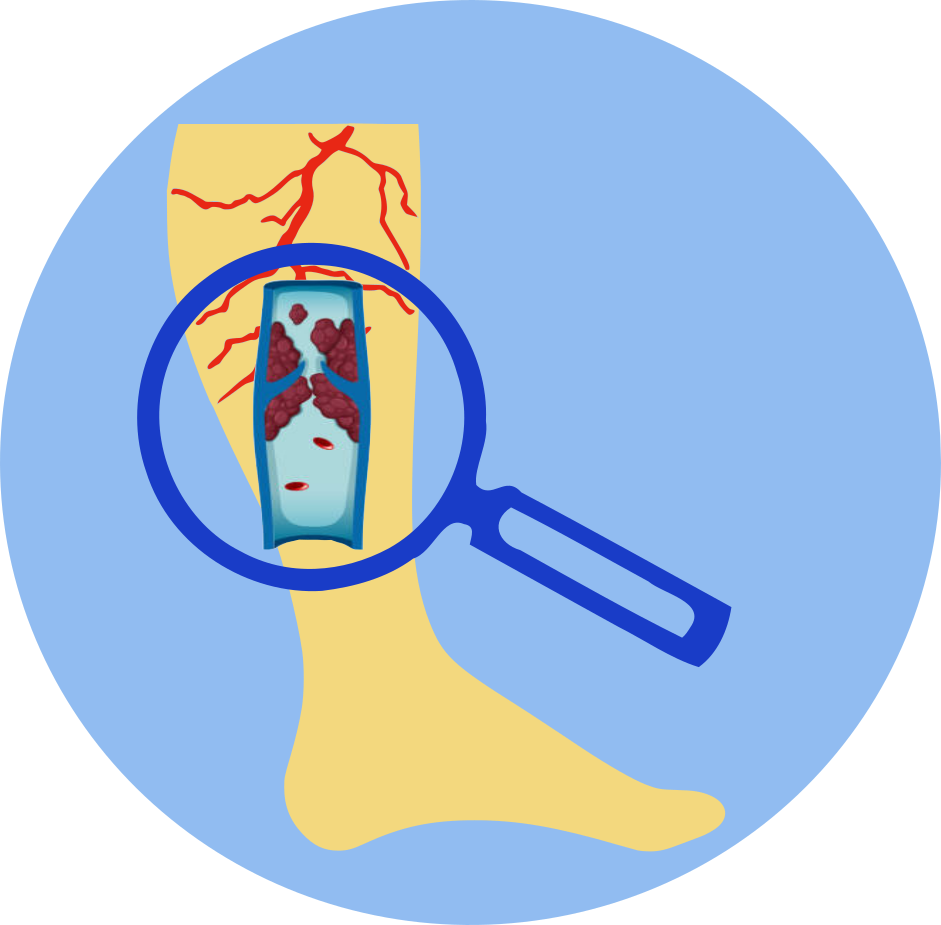
- Estrogens increase the risk of breast cancer, stroke, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and pulmonary embolism (PE). The risks and benefits of estrogen therapy should be carefully considered in each individual case, and estrogen therapy should be used at the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible.
- Women with a history of breast cancer or other estrogen-sensitive cancers should not use conjugated estrogens.
- Conjugated estrogens should be used with caution in women with a history of cardiovascular disease, liver disease, gallbladder disease, or hypertriglyceridemia, as estrogen therapy may exacerbate these conditions.
- Estrogen therapy may increase the risk of dementia in postmenopausal women over the age of 65.
- Women using conjugated estrogens should have regular breast exams and mammograms and should self-examine their breasts monthly.
Contraindication
Conjugated estrogen is contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to any component of the medication.
None known.
Conjugated estrogens are contraindicated in the following conditions:
- Known or suspected pregnancy
- Active or past history of breast cancer
- Known or suspected estrogen-dependent neoplasia
- Active or past history of DVT, PE, or arterial thromboembolic disease
- Active or past history of liver disease or hepatic impairment
- Undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding



 Bangla
Bangla English
English