Medicine details
| Image |  |
| Name | Diaplus 5 |
| Dosage | Tablet |
| Generic Name | Glipizide |
| Classes |
Antidiabetic Agent Metabolic Agent Sulfonylurea |
| Diseases |
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Hormonal Disorder |
| Company | Pacific Pharmaceuticals Ltd. |
Drug Package Details
| Strength | 5 mg |
| Storage Condition | |
| Origin Country | Bangladesh |
| Commercial Pack | 50 |
| Price per pack | ৳ 100.00 |
| Cost per pack | ৳ 88.00 |
| Package unit | 10 tabs strip |
| Price per unit | ৳ 2.00 |
| Cost per unit | ৳ 1.76 |
| Discount | 0 |
| Coupon | |
| Remarks |
Glipizide
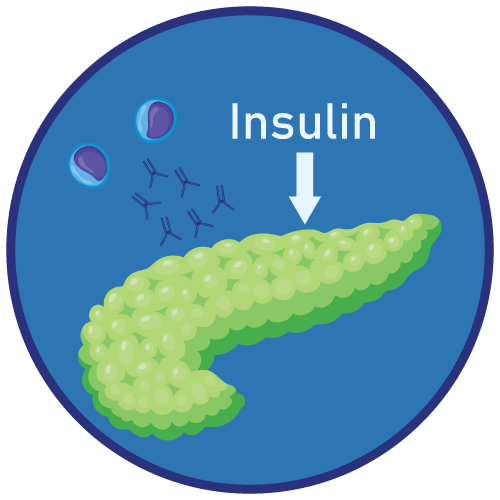
Glipizide is an oral hypoglycemic drug belonging to the class sulfonylureas. It works by closing K+ channels of the pancreatic beta cells which stimulates the release of insulin from the cells, thereby increasing the plasma insulin concentration. Glipizide also enhances the insulin sensitivity of peripheral cells.
Glipizide is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
There is no set dosage regimen for treating diabetes with Glipizide or any other hypoglycemic agent. In addition to the usual monitoring of urinary glucose, the patient's blood glucose must be monitored on a regular basis to determine the patient's minimum effective dose.
- Initial dose: The starting dose is 5 mg, taken before breakfast. 2.5 mg may be started in geriatric patients or those with liver disease.
- Titration: Dosage adjustments should be made in 2.5–5 mg increments, as determined by blood glucose response. A few days should elapse between titration steps. The maximum once-daily recommended dose is 15 mg. Doses greater than 15 mg should be divided and administered before meals with adequate caloric content. The maximum daily recommended dose is 40mg.
- Maintenance: Some patients may respond well to a once-a-day regimen, while others respond better to divided dosing. Above 15 mg, total daily doses should be divided. Long-term patients have received total daily doses in excess of 30 mg on a daily basis with no adverse effects. To avoid hypoglycemic reactions, initial and maintenance dosing should be conservative in elderly patients, debilitated or malnourished patients, and patients with impaired renal or hepatic function.
- Patients Receiving Insulin: If a patient's daily insulin requirement is less than 20 units, insulin can be stopped and Glipizide therapy can begin at usual dosages. Glipizide titration steps should be separated by several days.
If a patient's daily insulin requirement exceeds 20 units, the insulin dose should be reduced by half, and Glipizide therapy can begin at the usual dosages. Subsequent insulin dosage reductions should be based on individual patient response. Glipizide titration steps should be separated by several days.
Side effects associated with the drug are uncommon. The following adverse reactions have been reported-
- Hypoglycemia
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Erythema
- Urticaria
- Leukopenia
- Agranulocytosis
- Hepatic porphyria
- Disulfiram like reactions
The administration of oral hypoglycemic drugs has been reported to be associated with increased cardiovascular mortality as compared to treatment with diet alone or diet plus insulin.
- There have been no clinical studies demonstrating conclusive evidence of Glipizide or any other anti-diabetic drug lowering macrovascular risk.
- In patients with impaired renal and/or hepatic function, Glipizide metabolism and excretion may be slowed. Hypoglycemia may be prolonged in such patients, and appropriate management should be instituted.
- All sulfonylurea medications can cause severe hypoglycemia. To avoid hypoglycemic episodes, proper patient selection, dosage, and instructions are essential. Glipizide levels in the blood may be elevated due to renal or hepatic insufficiency, and the latter may also reduce gluconeogenic capacity, both of which increase the risk of serious hypoglycemic reactions.
- When a patient stabilized on any diabetic regimen is exposed to stress such as fever, trauma, infection, or surgery, a loss of control may occur. At such times, it may be necessary to discontinue Glipizide and administer insulin.
Contraindication
- Known hypersensitivity to the drug.
None known.
Contraindicated in-
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus
- diabetic ketoacidosis (with or without coma)




 Bangla
Bangla English
English