Medicine details
| Image |  |
| Name | Sudorin |
| Dosage | Tablet |
| Generic Name | Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride |
| Classes |
Cardiovascular Agent Respiratory Agent Decongestant Nasal Preparation Vasopressor |
| Diseases |
Congestion Nasal Problem |
| Company | Incepta Pharmaceuticals Ltd. |
Drug Package Details
| Strength | 60 mg |
| Storage Condition | |
| Origin Country | Bangladesh |
| Commercial Pack | 100 |
| Price per pack | ৳ 200.00 |
| Cost per pack | ৳ 176.00 |
| Package unit | 10 tabs strip |
| Price per unit | ৳ 2.00 |
| Cost per unit | ৳ 1.76 |
| Discount | 0 |
| Coupon | |
| Remarks |
Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride
Pseudoephedrine is a sympathomimetic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes. The sympathomimetic effect of pseudoephedrine produces vasoconstriction which in turn relieves nasal congestion.
- Adults and children over 12 years: One tablet if necessary, up to four times daily at intervals of not less than 4 hours.
- Children under 12 years: Not recommended.
- Elderly: There is no need for dosage reduction in the elderly.
Adverse effects may include-
- dry mouth
- anxiety
- restlessness
- tremor
- insomnia
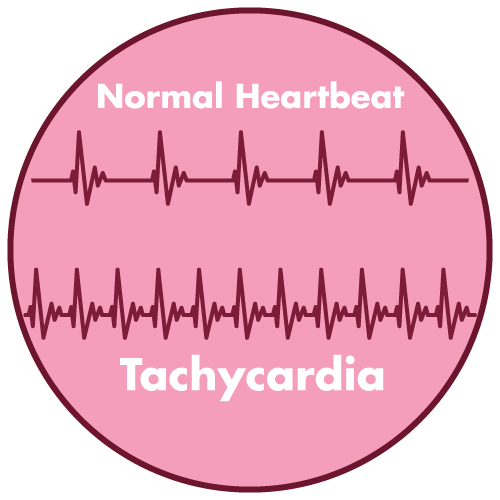
- tachycardia
- cardiac arrhythmias
- skin rashes
- Products containing pseudoephedrine may cause severe skin responses, such as acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP). With fever, numerous, small, largely non-follicular pustules, and a widespread edematous erythema that is primarily concentrated on the skin folds, trunk, and upper extremities, this acute pustular eruption may appear within the first two days of treatment. Patients need to be closely watched. Decongestant Tablets should not be administered if pyrexia, erythema, or numerous tiny pustules are seen. Instead, appropriate action should be taken.
- Pseudoephedrine has been linked to some cases of ischaemic colitis. If sudden abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, or other symptoms of ischaemic colitis develop, discontinue pseudoephedrine and seek medical advice.
- Pseudoephedrine has been linked to cases of ischemic optic neuropathy. If you experience sudden loss of vision or decreased visual acuity, such as scotoma, you should stop taking pseudoephedrine.
- Pseudoephedrine should be avoided in patients with cardiovascular disease, hypertension, severe renal impairment, diabetes mellitus, closed angle glaucoma, hyperthyroidism, prostatic enlargement and phaeochromocytoma.
Contraindication
Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to pseudoephedrine.
None known.
None known.




 Bangla
Bangla English
English