| Name | Betahistine Mesilate |
| Classes |
Central Nervous System Agent |
| Diseases |
CNS Disorder Hearing Loss Nausea Tinnitus (Ear Buzzing) Vertigo |
Betahistine Mesilate
Betahistine Mesilate is an antivertigo agent that is used to treat vertigo associated with Ménière's disease. Betahistine's mechanism of action is multifactorial. Ménière's disease is thought to be caused by a disruption in the ear's endolymphatic fluid homeostasis. Betahistine is primarily a histamine H1-receptor agonist. The stimulation of H1-receptors in the inner ear causes a vasodilatory effect, increasing blood vessel permeability and decreasing endolymphatic pressure; this action prevents the rupture of the labyrinth, which can contribute to Ménière's disease-related hearing loss. Betahistine is also said to relieve vertigo symptoms by reducing asymmetrical functioning of sensory vestibular organs and increasing vestibulocochlear blood flow. In addition to the mechanisms described above, betahistine acts as a histamine H3-receptor antagonist, increasing the turnover of histamine from postsynaptic histaminergic nerve receptors and, as a result, increasing H1-agonist activity.
Betahistine is indicated for treatment of Ménière's syndrome, symptoms of which may include-
- vertigo
- tinnitus
- hearing loss
- nausea
The initial oral dose is 8 to 16 mg three times per day, preferably with meals. Maintenance doses are typically between 24 and 48 mg per day. The daily dose should be divided into two or three equal doses throughout the day. The daily dose should not be more than 48 mg. Dosage can be adjusted to meet the needs of each individual patient.
Common side effects of betahistine include-
- headache
- nausea
- dyspepsia
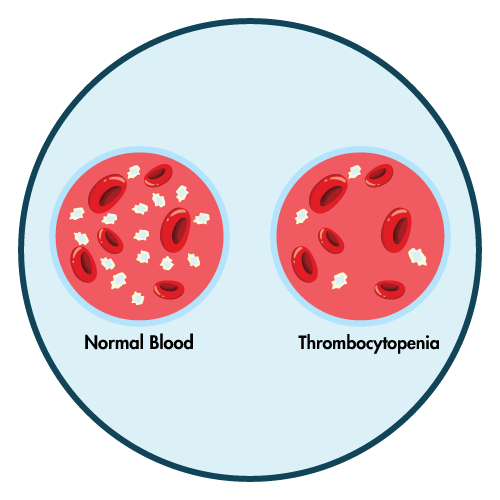
- thrombocytopenia
- Because of the occasional dyspepsia seen in betahistine patients, patients with peptic ulcers or a history of peptic ulceration should be treated with caution.
- Patients with bronchial asthma and peptic ulcers should be closely monitored during betahistine treatment.
- Betahistine should be used with caution in patients who have urticaria, rashes, or allergic rhinitis due to the risk of exacerbating these symptoms.
- Patients with severe hypotension should exercise caution.
Contraindication
Betahistine mesilate is contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to any component of the product.
None known.
Betahistine is contraindicated in patients with phaeochromocytoma.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English