| Name | Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate |
| Classes |
Dermatological/Topical Agent Hormonal Agent Steroid Astringent Glucocorticoid |
| Diseases |
Allergy Asthma Eczema Inflammatory Skin Disease Itching Leukemia Lupus Multiple Sclerosis Psoriasis Redness Rheumatoid Arthritis Swelling Ulcerative Colitis |
Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate
Betamethasone sodium phosphate belongs to a class of drugs, called the glucocorticoids. It is a synthetic glucocorticoid. Natural glucocorticoids (hydrocortisone and cortisone), which have salt-retaining characteristics, are employed in adrenocortical deficit replacement therapy. Their synthetic analogs are largely employed for anti-inflammatory actions in a variety of organ system illnesses.
Glucocorticoids have a wide range of metabolic consequences. Furthermore, they alter the immune system's reaction to a variety of stimuli.
Betamethasone sodium phosphate is usually used topically as eye and nasal drops.
- After clinical exclusion of bacterial, viral, or fungal infections, short-term treatment of steroid responsive inflammatory diseases of the eye.
- Inflammation of the ear or nose that is not infectious.
- Nasal
-
- Adult: For non-infected cases of the nose: As 0.1% betamethasone Na phosphate drops: Apply 2-3 drops into each nostril twice or thrice a day as required. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest possible time. Discontinue if there is no clinical response within 7 days of treatment.
- Ophthalmic
- Adult: For short-term treatment of steroid-responsive cases: As 0.1% betamethasone Na phosphate drops: Initially, apply 1-2 drops into the affected eye(s) every 1-2 hours, then reduce frequency once the condition is under control. As 0.1% betamethasone Na phosphate ointment: Apply 2-4 times daily; alternatively, doses may be applied at night. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest possible time. Discontinue if there is no clinical response within 7 days of treatment.
| Eye Drops | |
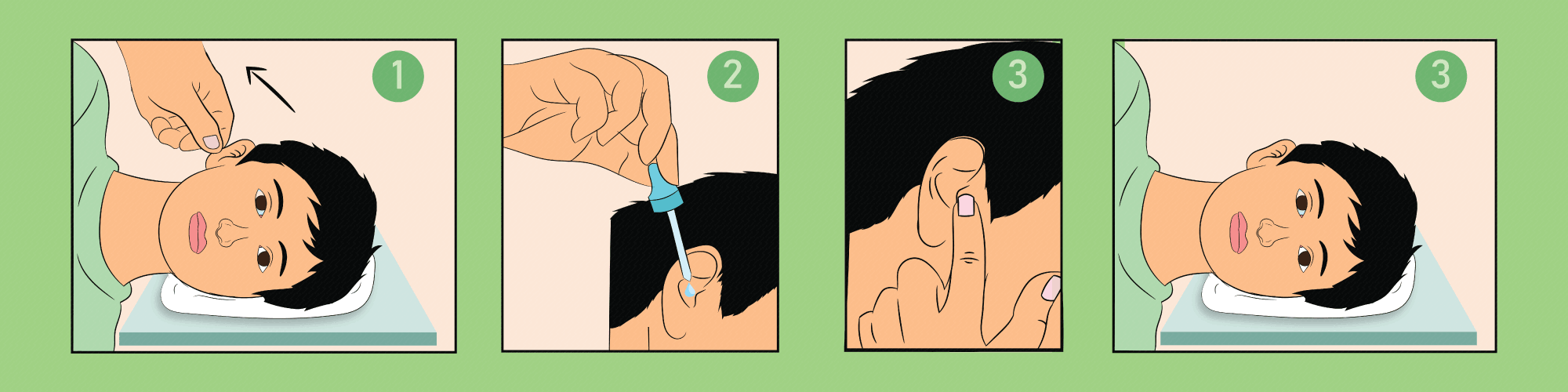
| Ear Drops |
Betamethasone sodium phosphate can cause the following side effects-
- irritation
- burning
- stinging
- itching
- dermatitis
- corneal ulceration
- posterior subcapsular cataracts (prolonged use)
- keratitis
- Undiagnosed red eyes should never be treated with topical corticosteroids.
- Ophthalmic treatment with corticosteroid preparations should not be repeated or continued without regular monitoring to rule out increased intraocular pressure, cataract formation, or infection.
Contraindication
Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to betamethasone or other glucocorticoids, such as-
There is no known contraindications of methyl prednisolone in terms of food and drinks.
Contraindicated in patients with systemic fungal infection.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English