| Name | Tinidazole |
| Classes |
Antiinfective Agent Antiprotozoal / Amebicide |
| Diseases |
Infectious Disease Parasitic Infection |
Tinidazole
Tinidazole is a nitroimidazole anti-infective agent. In Trichomonas, a ferredoxin-mediated electron transport mechanism reduces the nitro group of tinidazole. The antiprotozoal activity is thought to be due to the free nitro radical formed as a result of this reduction.
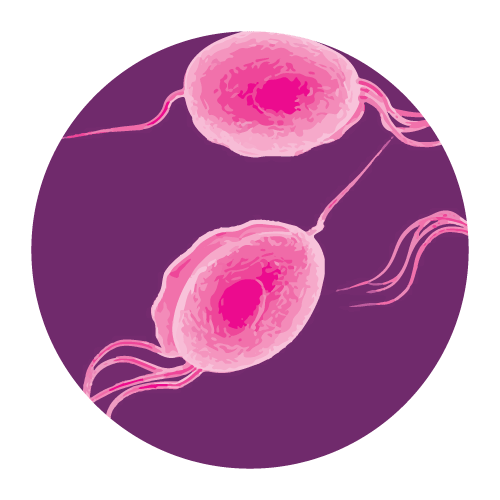
- For the treatment of trichomoniasis caused by T. vaginalis in both female and male patients.
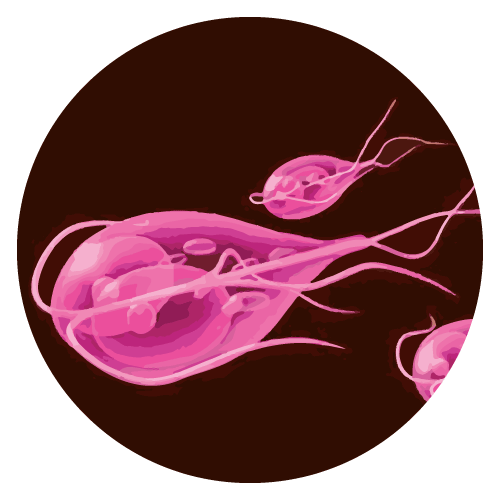
- Also for the treatment of giardiasis caused by G. duodenalis in both adults and pediatric patients
- For the treatment of intestinal amebiasis and amebic liver abscess caused by E. histolytica in both adults and pediatric patients
Amoebiasis:
- 500 mg twice a day for 5 days in adults.
- Children: 10-25 mg per kilogram of body weight, split into two doses.
Dysentery caused by amoebic bacteria:
- Adults should take 1.5 gm once a day for three days.
- For children, take 40 mg per kilogram of body weight once a day for three days.
Giardiasis:
- Adults should take 1.5 gm once a day for 1-2 days.
- For children, take 40 mg per kilogram of body weight for two days.
Trichomoniasis:
- Use 1.5 gm once a day or 500 mg twice a day for five days. In addition, the sexual partner should be treated at the same time.
For bacterial vaginosis, take three 500 mg tablets in one dosage or one 500 mg tablet once a day for 5-7 days.
Side effects associated with the drug are as follows-
- vaginal itching or burning;
- erythema
- white or yellow vaginal discharge (may be odorless)
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach pain
- headache
- a bitter or metallic taste in your mouth
Dizziness, vertigo, uncoordination, and ataxia have all been reported as a result of compounds with comparable chemical structures. If abnormal neurological signals arise while taking tinidazole, the medication should be stopped. Tinidazole is contraindicated during the first trimester of pregnancy and throughout lactation. While there is no indication that tinidazole is dangerous during pregnancy, it must be used during the latter two trimesters if the potential benefits outweigh the risk to the mother and fetus. Tinidazole is secreted in breast milk at levels comparable to those found in serum. For up to 72 hours after injection, tinidazole can be identified in breast milk. Breast-feeding should be stopped throughout tinidazole treatment and for 3 days after the last dosage.
Contraindication
Tinidazole should not be administered to patients with known hypersensitivity to the compound or similar compounds such as-
Avoid concomitant use of alcohol with tinidazole as it may cause flushing, nausea, vomiting, and headaches.
Contraindicated in-
- blood dyscrasias
- organic neurological disorders
 Bangla
Bangla English
English