| Name | Tobramycin |
| Classes |
Antiinfective Agent Antibiotic Dermatological/Topical Agent Topical Antiinfective Agent Respiratory Agent Ophthalmic Preparation Aminoglycoside |
| Diseases |
Eye Infection Ophthalmic Disease |
Tobramycin
Tobramycin is an antibiotic of the aminoglycoside class. It kills bacteria by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis.
Tobramycin is indicated for the following infections caused by susceptible strains of bacteria-
- Septicemia
- Bronchitis
- Pneumonia
- Meningitis
- Gastrointestinal infections
- Bone infection
- Skin infection
- Urinary tract infection
Tobramycin ophthalmic drops and ointment is indicated for-
Intravenous infusion:
- Administration for Patients with Normal Renal Function:
- Adults with Serious Infections 3 mg/kg/day in 3 equal doses every 8 hours.
- Adults with Life-Threatening Infections:
Up to 5 mg/kg/day may be administered in 3 or 4 equal doses. The dosage should be reduced to 3 mg/kg/day as soon as clinically indicated. To prevent increased toxicity due to excessive blood levels, dosage should not exceed 5 mg/kg/day unless serum levels are monitored. - Pediatric patients (greater than 1 week of age):
6 to 7.5 mg/kg/day in 3 or 4 equally divided doses (2 to 2.5 mg/kg every 8 hours or 1.5 to 1.89 mg/kg every 6 hours).
Ophthalmic drops/ointments:
- Drops: In mild to moderate infections, instill 1 or 2 drops every 4 hours into the infected eye(s). In severe infections, instill 2 drops per hour into the infected eye(s) until symptoms improve.
- Ointments: Apply a small amount 2-3 times daily into the conjunctival sac if you have a mild to moderate infection (s).
Apply a small amount 3-4 times daily into the conjunctival sac(s) in severe cases of infection until symptoms improve, then gradually reduce the dose. - Dosage adjustment is required for renally impaired patients.
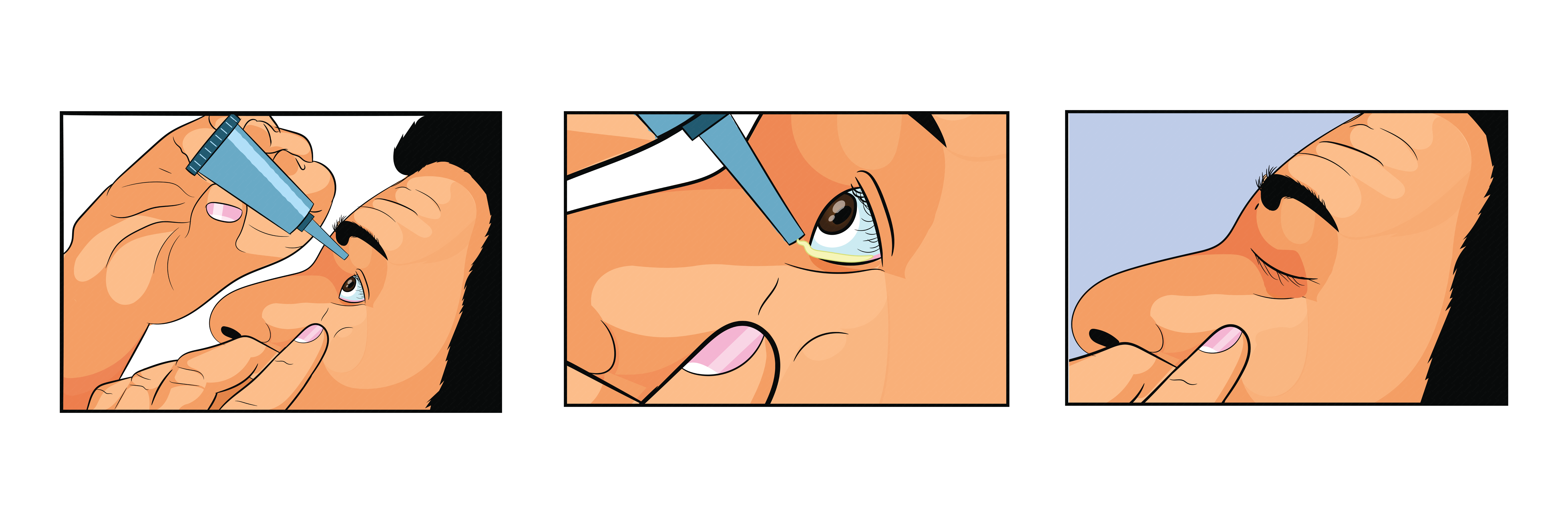
How to apply eye drops:
Tobramycin can cause the following side effects:
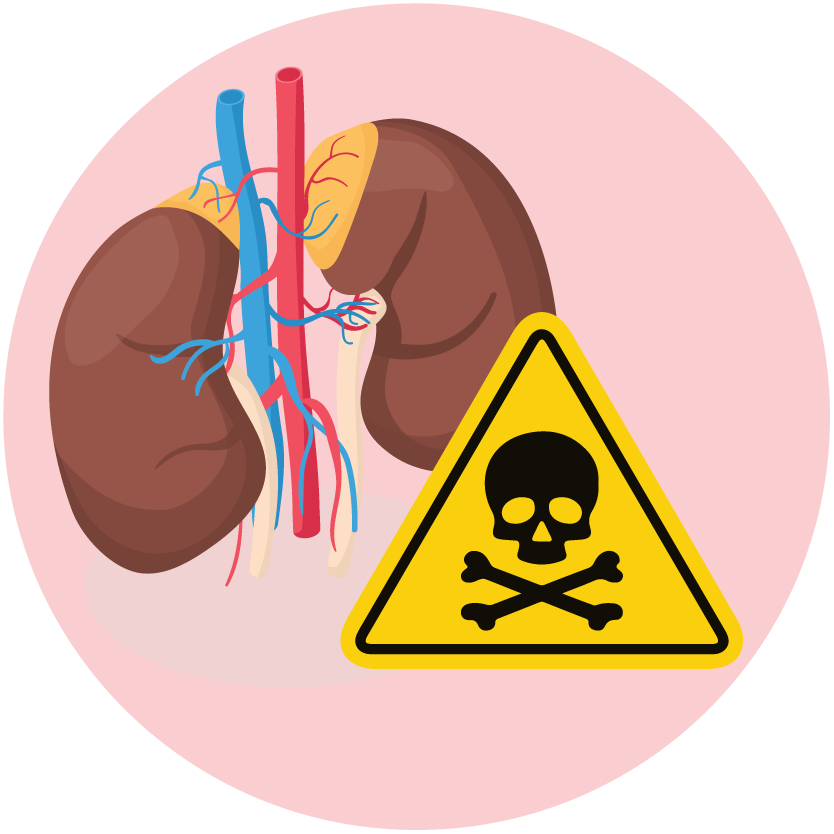
- Nephrotoxic
- Ototoxic
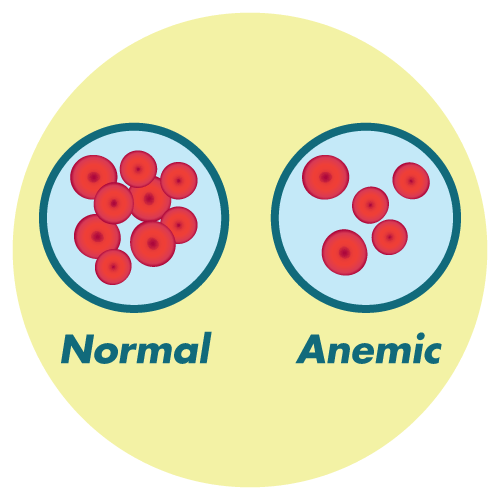
- Anemia
- Rash
- Fever
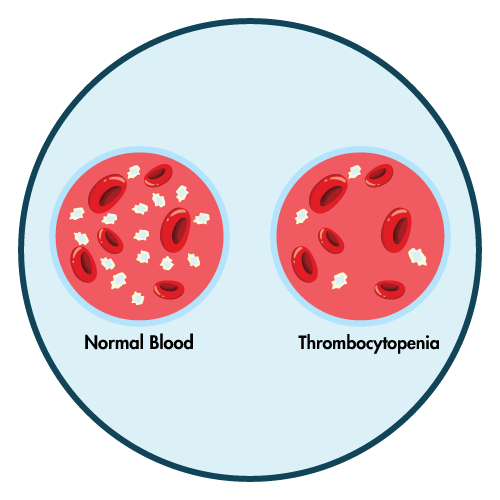
- thrombocytopenia
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Confusion
- Eosinophilia
- Because tobramycin injection and other aminoglycosides have the potential to cause ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity, patients receiving these medications should be closely monitored.
- It is possible to develop neurotoxicity, which manifests as both auditory and vestibular ototoxicity. The changes in hearing are permanent, usually bilateral, and may be partial or complete.
- Patients with preexisting renal injury and those with normal renal function who are given aminoglycosides for longer periods of time or at higher doses than indicated may develop eighth-nerve impairment and nephrotoxicity.
Contraindication
A hypersensitivity to any aminoglycoside is a contraindication to the use of tobramycin, such as-
Tobramycin is contraindicated in patients with severe renal problems.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English