| Name | Bisacodyl |
| Classes |
Gastrointestinal Agent Laxatives |
| Diseases |
Constipation Gastrointestinal Disease |
Bisacodyl
Bisacodyl is a stimulant laxative that promotes bowel movement by increasing the contraction of the intestinal muscles and stimulating the secretion of fluids in the colon. It works by directly stimulating the nerve endings in the intestinal wall and increasing the level of cyclic AMP, resulting in the increased peristaltic activity and secretion of water and electrolytes into the bowel lumen.
Bisacodyl is indicated for the treatment of constipation and for bowel preparation prior to diagnostic procedures such as colonoscopy.
The dosage and administration of bisacodyl depend on the age and condition of the patient. The medication is usually taken orally, as a tablet or suppository, with or without food. The recommended dose for adults is 5-15 mg daily, and for children 2.5-5 mg daily. For bowel preparation, a higher dose may be required, and the medication is usually taken the night before the procedure.
The most common adverse reactions associated with bisacodyl include-
abdominal cramps
diarrhea
nausea.
Rarely, the medication can cause severe abdominal pain, electrolyte disturbances, and dehydration. Prolonged use or overuse of bisacodyl can lead to severe dehydration, malnutrition, and metabolic disturbances.
-
Inflammatory bowel disease (e.g. ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease): Stimulant laxatives such as bisacodyl may exacerbate symptoms of these conditions and should be used with caution.
-
Electrolyte imbalances: Prolonged or excessive use of bisacodyl can cause loss of fluids and electrolytes, which may lead to imbalances in potassium, sodium, and other electrolytes. Patients with kidney disease or heart disease may be more susceptible to these effects.
-
Dehydration: The loss of fluids and electrolytes caused by bisacodyl can lead to dehydration, which may be more severe in elderly patients, children, and those with underlying medical conditions.
-
Rectal bleeding: Patients experiencing rectal bleeding or those with a history of rectal bleeding should avoid using bisacodyl suppositories.
-
Bowel obstruction: Bisacodyl should not be used in patients with intestinal obstruction or fecal impaction.
-
Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Bisacodyl should be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding only if directed by a healthcare provider.
-
Laxative dependence: Prolonged use or misuse of bisacodyl can lead to laxative dependence, a condition where the body becomes dependent on the medication to produce bowel movements. This can cause serious gastrointestinal disorders and may require medical treatment to overcome
Contraindication
Bisacodyl is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to bisacodyl or its components.
Bisacodyl should not be used in patients with-
- inflammatory bowel disease
- appendicitis
- intestinal obstruction
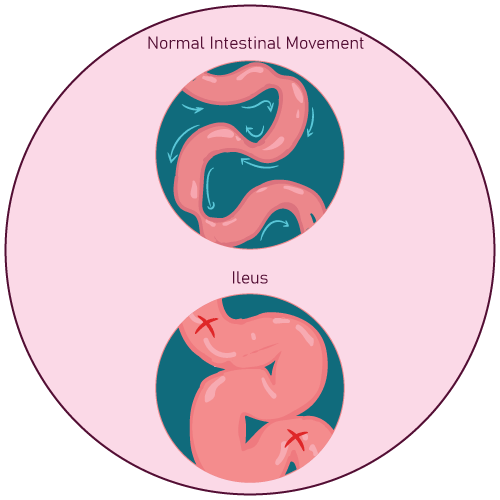
- ileus
 Bangla
Bangla English
English