| Name | Urokinase |
| Classes |
Coagulation Modifier Haematological Agent Thrombolytic |
| Diseases |
Blood Disorder Clotting |
Urokinase
Urokinase is a thrombolytic medication that works by converting plasminogen to plasmin, which is an enzyme that degrades fibrin, the protein that forms the matrix of blood clots. Plasmin breaks down fibrin into smaller fragments, which can then be cleared by the body's natural clotting and fibrinolytic systems. Urokinase specifically targets and activates plasminogen molecules that are bound to fibrin, which helps to focus the fibrinolytic activity of plasmin on the thrombus or clot, while minimizing the risk of systemic bleeding.
Urokinase is indicated in adults:
- For the lysis of acute massive pulmonary emboli, defined as obstruction of blood flow to a lobe or multiple segments.
- For the lysis of pulmonary emboli accompanied by unstable hemodynamics, i.e., failure to maintain blood pressure without supportive measures.
The recommended dosage of urokinase is based on patient weight and is administered as an initial intravenous bolus of 4400 international units (IU) per kilogram, followed by a continuous infusion of 4400 IU per kilogram per hour for up to 12 hours or until complete thrombolysis is achieved. The total dosage should not exceed 5 million IU.
The major side effects associated with urokinase are as follows:
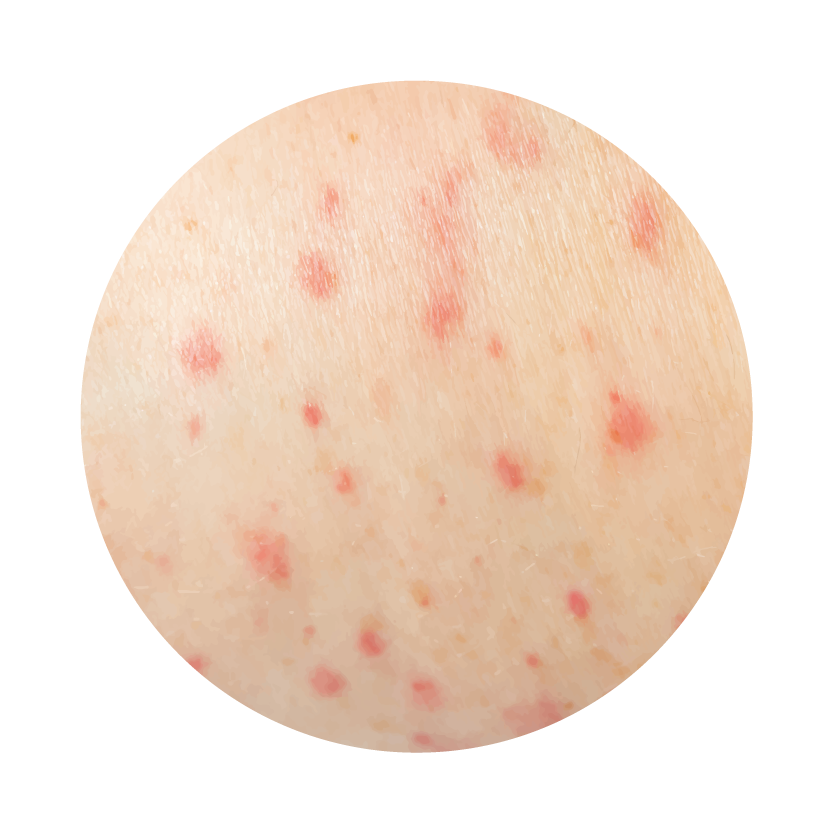
- Bleeding
- Allergic reactions
- Fever
- Hypotension (low blood pressure)
- Back pain
- Chest pain
- Injection site reactions
- Nausea and vomiting
Urokinase should be used with caution in patients with a history of recent gastrointestinal bleeding, recent stroke or other cerebrovascular disease, severe liver or kidney disease, or bacterial endocarditis. In addition, urokinase should be used with caution in patients with a history of allergy or bronchial asthma. Urokinase should be administered only under the supervision of a healthcare provider experienced in the use of thrombolytic therapy.
Contraindication
Contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to the product.
None known.
Because thrombolytic therapy increases the risk of bleeding, Urokinase is contraindicated in the situations listed below
- Active internal bleeding
- Recent (e.g., within two months) cerebrovascular accident
- Recent (e.g., within two months) intracranial or intraspinal surgery
- Recent trauma including cardiopulmonary resuscitation
- Intracranial neoplasm, arteriovenous malformation, or aneurysm
- Known bleeding diatheses
- Severe uncontrolled arterial hypertension
 Bangla
Bangla English
English