| Name | Buparvaquone |
| Classes |
Cardiovascular Agent Diuretic Loop Diuretic |
| Diseases |
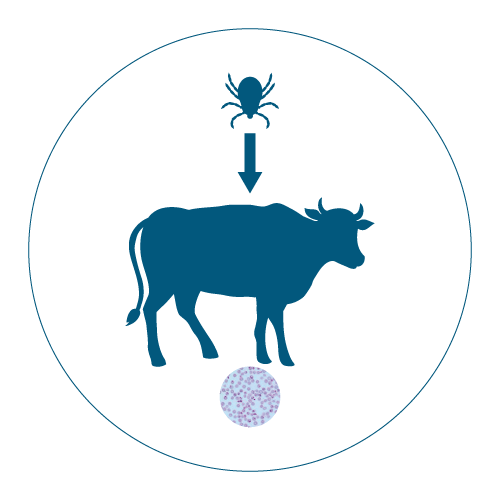
Corridor Disease East Coast Fever Theilerioosis Veterinary Disease |
Buparvaquone
Buparvaquone belongs to the class of antiprotozoal agents. Its mechanism of action involves interference with the electron transport chain in the mitochondria of protozoa, leading to the disruption of cellular respiration and subsequent death of the parasites.
Buparvaquone is indicated for the treatment of infections caused by Theileria annulata in bovines. It is specifically used to manage tropical theileriosis, a disease transmitted by ticks, and is effective against the intraerythrocytic forms of the parasite.
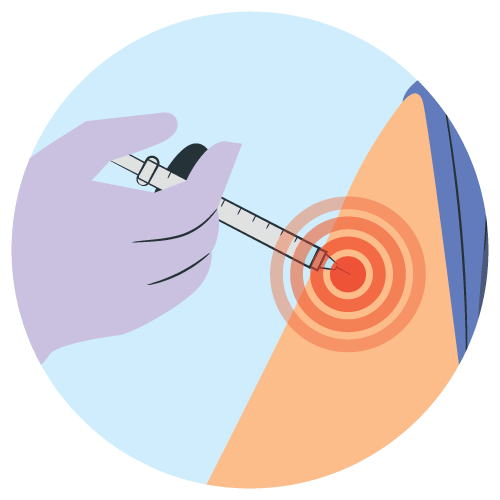
The dosage of Buparvaquone is typically based on body weight and should be administered under the supervision of a qualified veterinarian. Specific dosage regimens may vary, and it is essential to follow the veterinarian's instructions for the appropriate age and weight of the animal.
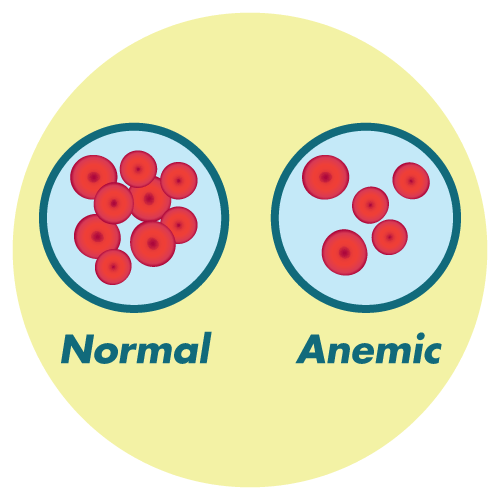
Common adverse reactions associated with Buparvaquone may include local reactions at the injection site, transient anorexia, and mild changes in hematology parameters. Infrequent adverse events may involve hypersensitivity reactions.
- Hypersensitivity: Buparvaquone may cause hypersensitivity reactions. Discontinue treatment if signs of hypersensitivity occur and administer appropriate therapeutic measures.
- Local Irritation: Monitor for local irritation at the injection site. In case of severe reactions, consult a veterinarian.
- Special Populations: Use with caution in animals with known pre-existing conditions, and adjust dosage as necessary.
Contraindication
Buparvaquone is contraindicated in animals with a known hypersensitivity to the drug.
None known.
None known.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English