| Name | Cefotaxime |
| Classes |
Antiinfective Agent Antibiotic Cephalosporine |
| Diseases |
Bronchitis Gonorrhea Infectious Disease Meningitis Otitis Pneumonia Sinusitis Tonsillitis Urethritis |
Cefotaxime
Cefotaxime is a 3rd gen cephalosporin that kills bacteria by inhibiting cell wall synthesis. It is a broad spectrum antibiotic.
Cefotaxime is indicated for the following infections-
- Infections of the lower respiratory tract
- Infections of the kidneys and urinary tract
- Infections of the skin and soft tissue
- Genital infections caused by gonococci, particularly when penicillin has failed or is unsuitable
- Intra-abdominal infections
- Lyme disease
- Acute Meningitis
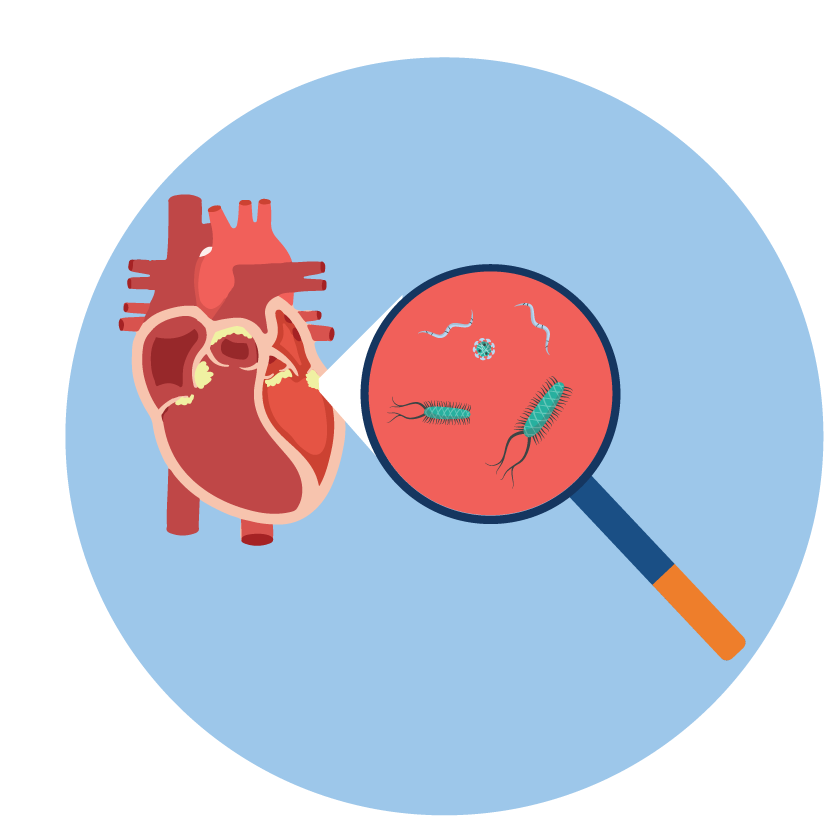
- Endocarditis
- Cefotaxime is available as Injection.
- The dosage and mode of administration are determined by the severity of the infection, the bacterium's sensitivity, and the patient's condition.
- Cefotaxime is given in 1 g doses every 12 hours to adults and children over the age of 12. The daily dose might be increased to 12 g in extreme situations. Daily doses of up to 6 g can be split into at least two separate 12 hours administrations. Higher daily doses must be divided into at least three to four separate administrations at eight or six hour intervals.
- Dosage in the Case of Impaired Renal Function: The maintenance dose is lowered to half the regular dose in patients with a creatinine clearance of 20ml/minute or less. A lowering of the maintenance dose to 1 g Cefotaxime (split into two individual administrations at 12 hour intervals) appears to be appropriate for patients with a creatinine clearance of 5 ml/minute or less. The following suggestions are based on adult experiences.
Side effects associated with Cefotaxime include-
- Pseudomembranous colitis
- Fever
- Rash
- Diarrhea
- Pain at injection site
- Eosinophilia
- Liver problems
- Phlebitis
- Cefotaxime should be used with caution in people who have had gastrointestinal disorders, especially colitis.
- In people who have a history of allergies or asthma, cefotaxime should be administered with caution.
- Cefotaxime has been linked to significant bullous skin reactions like Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
- Diarrhoea, especially if severe and/or chronic, and occurring during or shortly after therapy, could be a sign of Clostridium difficile-associated illness (CDAD). CDAD can range in severity from minor to life-threatening, with pseudomembranous colitis being the most severe.
Contraindication
Cefotaxime is contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to beta lactam antibiotics, such as-
 Bangla
Bangla English
English