| Name | Cimetidine |
| Classes |
Gastrointestinal Agent Antiulcerants H2 Blocker / Histamine-2 Receptor Antagonist |
| Diseases |
Anesthesia Dyspepsia Gastrointestinal Disease GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) Heart Burn Hemorrhoid Insect Bite Pain Sun Burn Ulcer |
Cimetidine
Cimetidine is a histamine H2-receptor antagonist that lowers pepsin production and suppresses both baseline and induced stomach acid secretion.
Cimetidine is indicated for the following condition-
- Benign gastric and duodenal ulceration
- Pancreatic insufficiency
- Prophylaxis of gastrointestinal hemorrhage from stress ulceration
- Prophylaxis of acid aspiration during general anesthesia
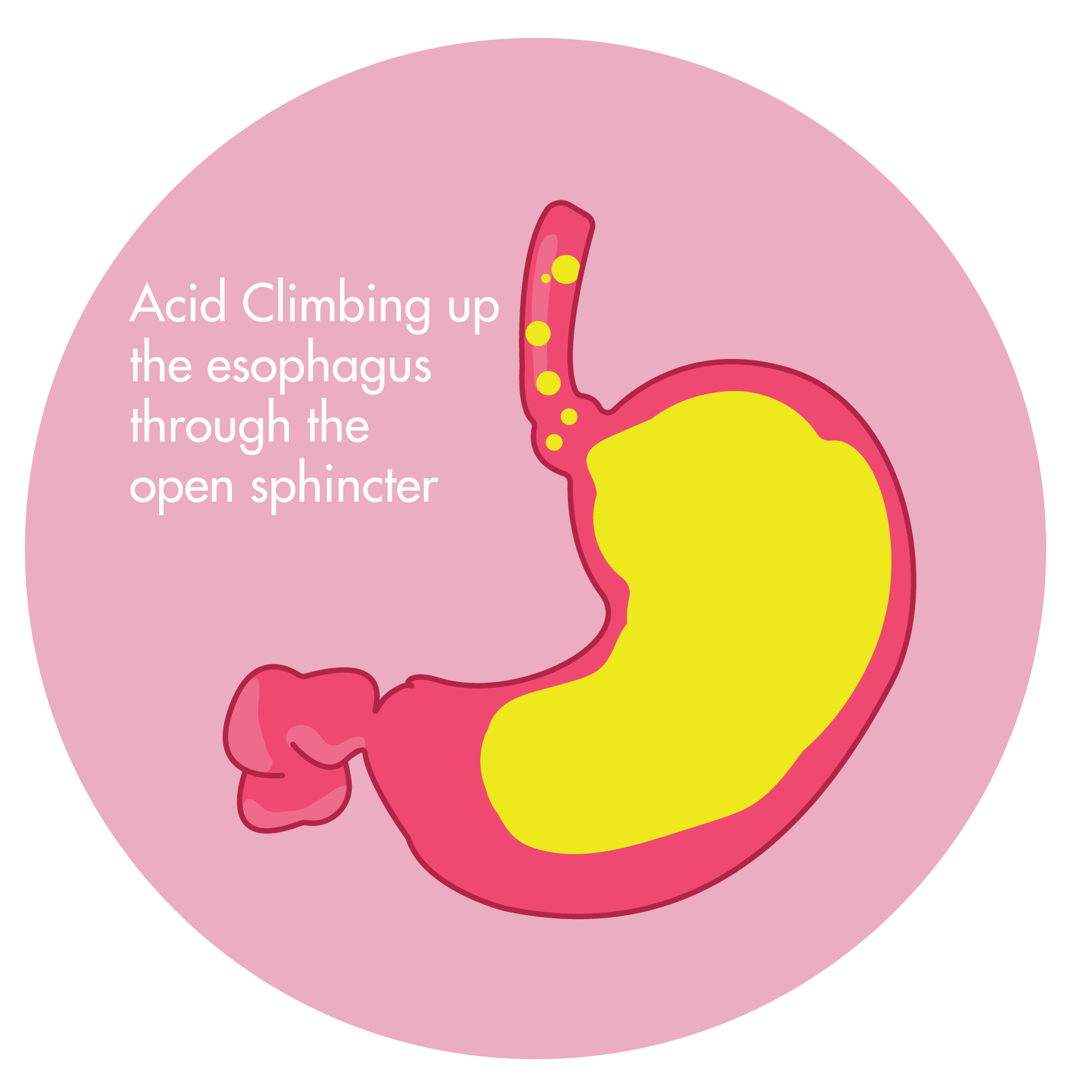
- Gastro-esophageal reflux disease
- Hypersecretory conditions, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
- Short bowel syndrome
Adults:
- Oral: The usual dosage is 400mg twice a day, with breakfast and at bedtime. For patients with duodenal or benign gastric ulceration, a single daily dose of 800mg at bedtime is recommended. Other effective regimens are 200mg three times a day with meals and 400mg at bedtime (1.0g/day) and, if inadequate, 400mg four times a day (1.6g/day), also with meals and at bedtime.
- In those individuals who benefit from lower gastric secretion, treatment can be continued for extended periods of time, and the dosage can be adjusted as needed to 400mg at bedtime or 400mg in the morning and at bedtime. Continued medication, usually 400mg at bedtime, can prevent relapse in individuals with benign peptic ulcer disease who responded to the initial course; 400mg in the morning and at evening has also been utilized.
-
In esophageal reflux disease, 400 mg four times a day, with meals and at bedtime, for four to eight weeks is recommended to heal esophagitis and relieve associated symptoms. In patients with very high gastric acid secretion (e.g. Zollinger-Ellison syndrome) it may be necessary to increase the dose to 400mg four times a day or in occasional cases further. Since Cimetidine may not give immediate symptomatic relief, antacids can be made available to all patients until symptoms disappear.
-
In the prophylaxis of hemorrhage from stress ulceration in seriously ill patients, doses of 200 - 400mg can be given every four to six hours by the oral route.
-
In patients thought to be at risk of acid aspiration syndrome, an oral dose of 400mg can be given 90-120 minutes before induction of general anesthesia or, in obstetric practice, at the start of labor. While such a risk persists, a dose of up to 400mg may be repeated (parenterally if appropriate) at four hourly intervals as required up to the usual daily maximum of 2.4g
Children under 12 years: Seek physician's advice.
Side effects associated with the use of cimetidine include-
- Vitamin B12 deficiency (prolonged use)
- Diarrhea
- Confusion
- Asthenia
- Myalgia
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Somnolence
- In patients with compromised renal function, dosage should be lowered based on creatinine clearance. The following doses are suggested:
-
- Creatinine clearance of 0 to 15ml per minute, 200mg twice a day;
- 15 to 30ml per minute, 200mg three times a day;
- 30 to 50ml per minute, 200mg four times a day;
- over 50 ml per minute, normal dosage.
- Cimetidine is removed by hemodialysis, but not to any significant extent by peritoneal dialysis.
- Care should be taken that patients with a history of peptic ulcer, particularly the elderly, being treated with Cimetidine and a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent are observed regularly.
- Malignancy should be eliminated by endoscopy and biopsy, if possible, before starting therapy with this preparation for any stomach ulcers, because Cimetidine pills can ease symptoms and aid in the superficial healing of gastric cancer. The ramifications of a possible diagnosis delay should be considered, especially in patients who are middle-aged or older and have new or recently modified dyspeptic symptoms.
-
When cimetidine is used in conjunction with coumarins, it is important to keep a close eye on the prothrombin time.
- When initiating or terminating concomitantly provided cimetidine, it may be necessary to alter the dosage of therapeutic drugs having a narrow therapeutic index, such as phenytoin or theophylline.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to Cimetidine or to any of the tablet's ingredients.
There is no known contraindications of Cimetidine Hydrochloride + Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride in terms of food and drinks.
There is no known contraindications of Cimetidine Hydrochloride + Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride in terms of health conditions.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English