| Name | Ethambutol |
| Classes |
Antiinfective Agent Antituberculosis Agent |
| Diseases |
Infectious Disease TB (Tuberculosis) |
Ethambutol
Ethambutol is classified as an antimycobacterial agent. The exact mechanism of action involves inhibiting the synthesis of mycobacterial cell wall components, particularly arabinogalactan synthesis. By disrupting the formation of the mycobacterial cell wall, Ethambutol exhibits bacteriostatic activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Ethambutol is indicated for the treatment of tuberculosis, either as a first-line agent in combination therapy or as a component of multidrug regimens.
- Initial Treatment: For patients without prior antituberculous therapy, administer Ethambutol at a dosage of 15 mg/kg (equivalent to 7 mg/lb) of body weight as a single oral dose every 24 hours. In recent studies, isoniazid has been concurrently administered in a single daily oral dose.
- Retreatment: In patients with a history of previous antituberculous therapy, provide Ethambutol at a dosage of 25 mg/kg (equivalent to 11 mg/lb) of body weight as a single oral dose every 24 hours. Concurrently, administer at least one other antituberculous drug for which the organisms have shown susceptibility based on appropriate in-vitro tests. Preferably, use drugs that have not been previously employed in the patient's treatment. After 60 days of Ethambutol administration at 25 mg/kg, reduce the dose to 15 mg/kg (equivalent to 7 mg/lb) of body weight, and administer as a single oral dose every 24 hours.
- It is advisable to conduct monthly eye examinations during the period when a patient is on a daily dose of 25 mg/kg.
Adverse reactions are listed in decreasing order of frequency:
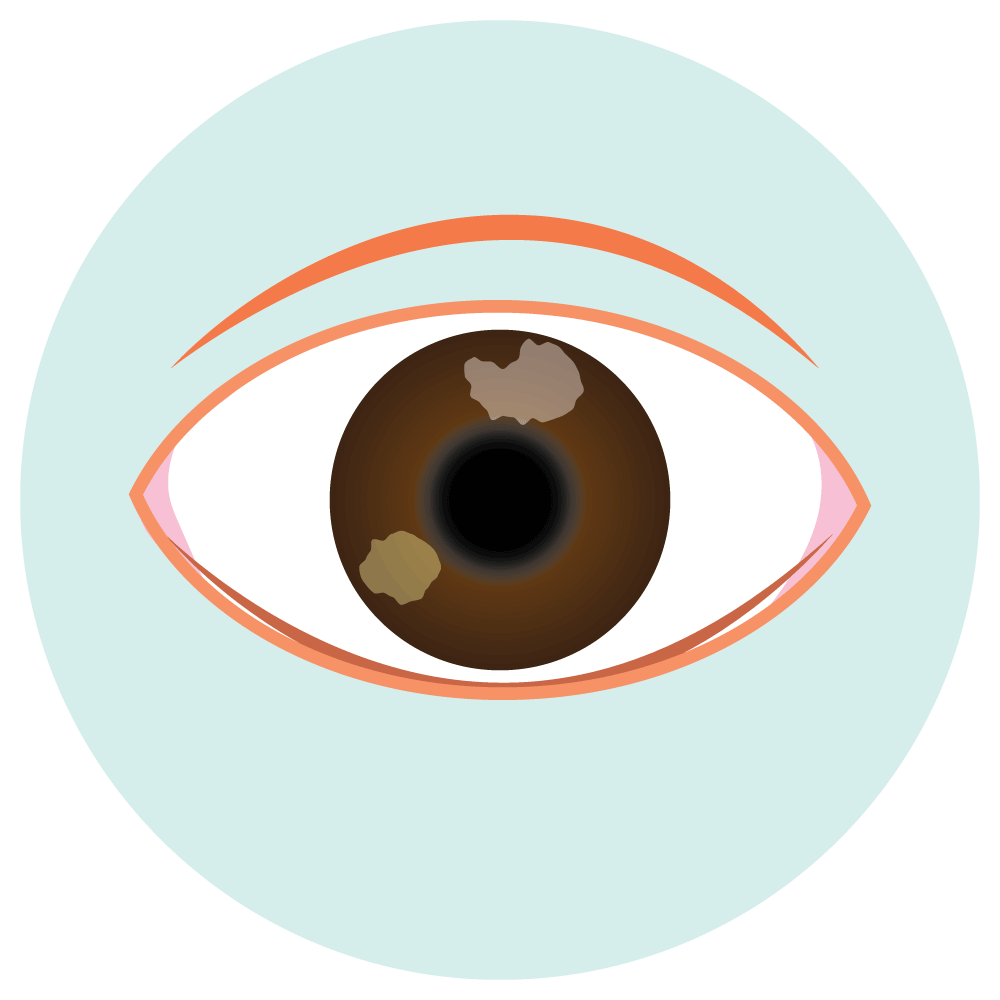
- Optic Neuritis
- Peripheral Neuropathy
- Hyperuricemia
- Arthralgia
- Gastrointestinal Disturbances
- Elevated Liver Enzymes
- Dermatologic Reactions
- Malaise
- Fever
- Anorexia
- Optic Neuritis: Regular monitoring of visual function is crucial, and if any visual disturbances occur, the healthcare provider should be notified immediately. Consideration of discontinuation may be necessary.
- Peripheral Neuropathy: Monitor for symptoms of peripheral neuropathy, such as numbness or tingling in the extremities. Dose adjustment or discontinuation may be needed.
- Hepatic Function: Regular monitoring of liver function is advisable, especially in patients with pre-existing liver conditions.
- Renal Function: Adjustments may be necessary in patients with impaired renal function.
- Hyperuricemia: Monitor uric acid levels, especially in patients with a history of gout.
Contraindication
Contraindicated in individuals with a known hypersensitivity to Ethambutol.
None known.
Avoid use in patients with pre-existing optic neuritis unless the benefits outweigh the risks.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English