| Name | Aminocaproic Acid |
| Classes |
Coagulation Modifier Haematological Agent Antifibrinolytic |
| Diseases |
Bleeding Bypass Surgery Cervical Cancer Circulatory Disorder Fibrinolysis Hemophilia Hepatic Cirrhosis |
Aminocaproic Acid
Aminocaproic Acid is a medication classified as an antifibrinolytic agent. Its mechanism of action involves inhibiting the breakdown of blood clots by preventing the activation of plasminogen to plasmin, an enzyme responsible for clot dissolution.
Aminocaproic Acid is indicated for the treatment and prevention of excessive bleeding or hemorrhage associated with various conditions, including:
- Surgical procedures where increased bleeding is anticipated
- Dental extractions in patients with bleeding disorders
- Hemorrhagic complications of fibrinolytic therapy
- Hemorrhage caused by excessive fibrinolysis or hyperfibrinolysis
- Bleeding disorders, such as hemophilia, von Willebrand disease, or uremia
- Prostatectomy-related bleeding
- Intravenous aminocaproic acid Injection is administered by infusion, utilizing the usual compatible intravenous vehicles (e.g., Sterile Water for Injection, Sodium Chloride for Injection, 5% Dextrose or Ringer’s Injection). Although Sterile Water for Injection is compatible for intravenous injection the resultant solution is hypo-osmolar. RAPID INJECTION OF aminocaproic acid INJECTION UNDILUTED INTO A VEIN IS NOT RECOMMENDED.
- For the treatment of acute bleeding syndromes due to elevated fibrinolytic activity, it is suggested that 16 to 20 mL (4 to 5 g) of aminocaproic acid Injection in 250 mL of diluent be administered by infusion during the first hour of treatment, followed by a continuing infusion at the rate of 4 mL (1 g) per hour in 50 mL of diluent. This method of treatment would ordinarily be continued for about 8 hours or until the bleeding situation has been controlled. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
Adverse reactions to Aminocaproic Acid may occur but are generally uncommon. The most common adverse reactions include:
- Gastrointestinal disturbances (such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea)
- Hypotension (low blood pressure)
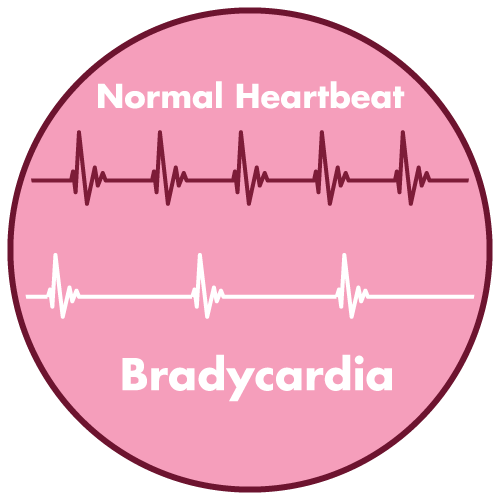
- Sinus bradycardia (slow heart rate)
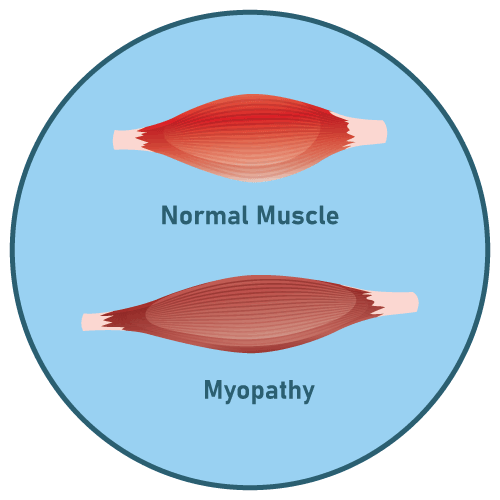
- Myopathy (muscle disease)
- Hypersensitivity reactions (rare)
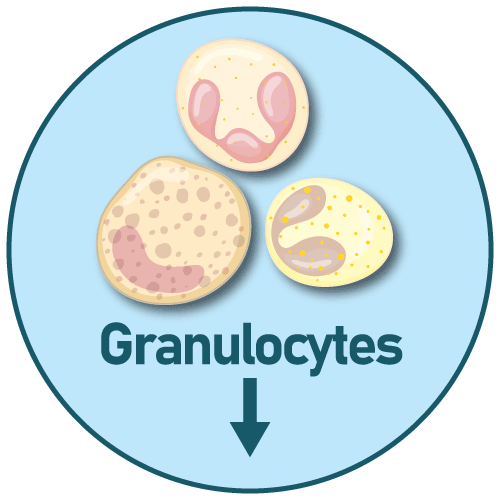
- Agranulocytosis
- Aminocaproic Acid should be used with caution in individuals with a history of thromboembolic events, as it may increase the risk of blood clot formation.
- Patients with renal impairment may require dosage adjustments and close monitoring due to the potential accumulation of Aminocaproic Acid.
- The medication should be used cautiously in patients with cardiac conditions, as it may affect heart rate and blood pressure.
- Aminocaproic Acid should not be used concurrently with thrombolytic agents unless the potential benefits outweigh the risks.
- The safety and efficacy of Aminocaproic Acid in pediatric patients, pregnant women, and breastfeeding mothers have not been fully established, and caution should be exercised when using the medication in these populations.
Contraindication
Aminocaproic Acid is contraindicated in individuals with hypersensitivity to any component of the formulation.
None known.
Aminocaproic Acid should not be used when there is evidence of an active intravascular clotting process. When there is uncertainty as to whether the cause of bleeding is primary fibrinolysis or disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), this distinction must be made before administering Aminocaproic Acid
 Bangla
Bangla English
English