| Name | Ivabradine |
| Classes |
Cardiovascular Agent Antianginal Agent |
| Diseases |
Angina Cardiovascular Disease Heart Failure |
Ivabradine
Ivabradine is a selective inhibitor of the hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels in the sinoatrial node, which leads to a reduction in the heart rate.
Ivabradine is indicated-
- To reduce the risk of hospitalization for worsening heart failure in adult patients with stable, symptomatic chronic heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction.
- For the treatment of stable symptomatic heart failure due to dilated cardiomyopathy in pediatric patients ages 6 months and older.
Adult and pediatric patients greater than 40 kg: Starting dose is 2.5 (pediatrics and vulnerable adults) or 5 mg twice daily with food. After 2 weeks of treatment, adjust dose based on heart rate. The maximum dose is 7.5 mg twice daily.
Pediatric Patients less than 40 kg: Starting dose is 0.05 mg/kg twice daily with food. Adjust dose at two-week intervals by 0.05 mg/kg based on heart rate. Maximum dose is 0.2 mg/kg (patients 6 months to less than 1 year old) or 0.3 mg/kg (patients 1 years old and older), up to a total of 7.5 mg twice daily.
The most common adverse reactions reported with ivabradine include-
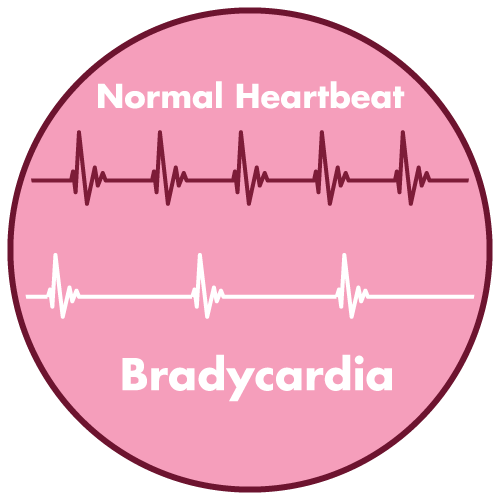
- bradycardia
- hypertension
- atrial fibrillation
- visual brightness
- phosphenes
Less common adverse reactions include dizziness, blurred vision, and headache.
- Ivabradine is contraindicated in patients with sick sinus syndrome, sinoatrial block, or third-degree atrioventricular block, unless a functioning demand pacemaker is present.
- Patients with severe hypotension, cardiogenic shock, acute myocardial infarction, unstable angina pectoris, or decompensated heart failure should not be treated with ivabradine.
- Ivabradine should be used with caution in patients with concomitant administration of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, as this may lead to an increase in ivabradine plasma concentration and adverse reactions.
- Patients with liver impairment should be closely monitored during treatment with ivabradine, as hepatic impairment can increase the bioavailability of ivabradine.
- Ivabradine should not be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding, as the safety and efficacy of the drug have not been established in these populations.
Contraindication
- Ivabradine is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity of ivabradine or any component of the formulation.
- Ivabradine is contraindicated in combination with strong cytochrome CYP3A4 inhibitors such as-
None known.
Ivabradine is contraindicated in the following conditions-
- Acute decompensated heart failure
- Sick sinus syndrome, sinoatrial block or 3rd degree AV block, unless a functioning demand pacemaker is present
- Clinically significant bradycardia
- Clinically significant hypotension
- Severe hepatic impairment
- Heart rate maintained exclusively by the pacemaker
 Bangla
Bangla English
English