| Name | Nebivolol |
| Classes |
Cardiovascular Agent Antihypertensive Beta-Adrenoceptor Blocker |
| Diseases |
Cardiovascular Disease Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) |
Nebivolol
Nebivolol belongs to a class of drugs called the beta-1 receptor blockers. It binds to the beta 1 receptors of the heart and reduces heart rate.
Nebivolol is indicated for the following conditions-
- Hypertension
- Chronic heart failure (CHF) :Treatment of stable mild and moderate chronic heart failure in addition to standard therapies in elderly patients ≥ 70 years.
The dose of Nebivolol must be tailored to the patient's specific needs. The suggested initial dose for most individuals is 5 mg once daily, with or without food, as monotherapy or in combination with other medications. The dose can be increased up to 40 mg at 2-week intervals for people who require further blood pressure lowering. It's unlikely that a more frequent dosing schedule will help.
Patients with renal impairment:
The recommended starting dose for people with renal insufficiency is 2.5 mg per day. The daily dose can be increased to 5 mg if necessary.
Patients with hepatic impairment:
There is a scarcity of data in patients with hepatic insufficiency or reduced liver function. As a result, Nebivolol should not be used in these individuals.
Geriatric patients:
The suggested beginning dose for patients over the age of 65 is 2.5 mg per day. The daily dose can be increased to 5 mg if necessary. However, due to the lack of experience with patients above the age of 75, vigilance should be exercised and these individuals constantly watched.
- Patients with coronary artery disease have experienced severe worsening of angina, myocardial infarction, and ventricular arrhythmias after abruptly discontinuing -blocker medication.
- Beta-blockers should not be given to people with bronchospastic disorders in general.
- Some hypoglycemia symptoms, particularly tachycardia, may be obscured by -blockers. Nonselective blockers may increase the severity of insulin-induced hypoglycemia and prolong the time it takes for serum glucose levels to return to normal.
- In patients with significant renal impairment, nebivolol clearance is reduced.
- In patients with significant hepatic impairment, nebivolol metabolism is reduced.
Contraindication
Contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to nebivolol or other beta blockers, such as-
Nebivolol is contraindicated is the following health conditions-
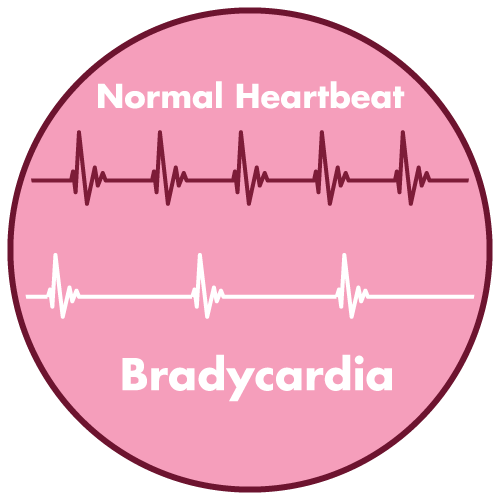
- Bradycardia (severe)
- Heart block
- Cardiogenic shock
- Decompensated cardiac failure
- Severe hepatic impairment
- Sick sinus syndrome
 Bangla
Bangla English
English