| Name | Neostigmine Methyl Sulphate |
| Classes | |
| Diseases |
CNS Disorder Myasthenia Gravis Postoperative Distention |
Neostigmine Methyl Sulphate
Neostigmine is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Acetylcholinesterase is the enzyme responsible for breaking down acetylcholine. Therefore, by blocking the enzyme, Neostigmine increases the acetylcholine concentration in the synaptic cleft or neuro-muscular junction.
Neostigmine Methyl Sulphate injection is indicated for the following conditions-
- Myasthenia Gravis
- antagonist to non-depolarizing neuromuscular blockade
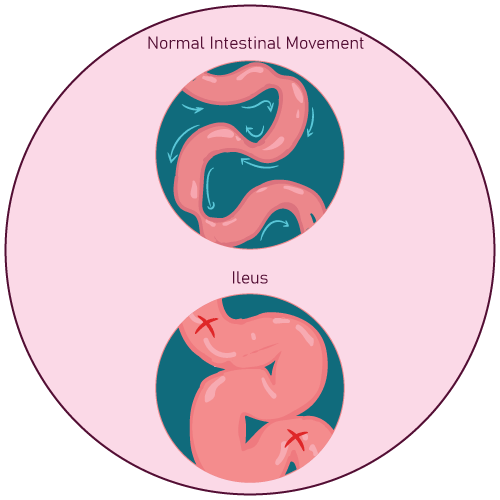
- Paralytic Ileus
- Post-operative Urinary Retention
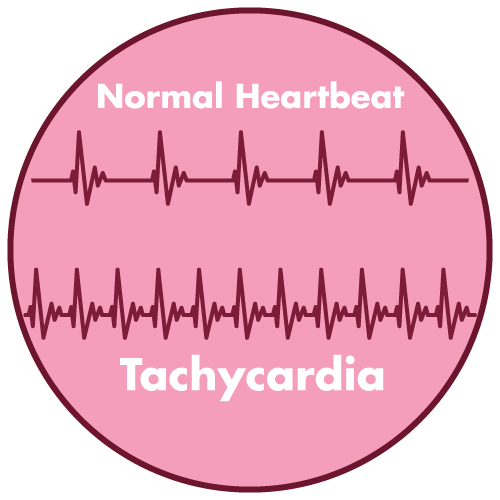
- Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia
- Should be administered by trained healthcare providers
- Peripheral nerve stimulator and monitoring for twitch responses should be used to determine when Neostigmine should be initiated and if additional doses are needed
- For reversal of NMBAs with shorter half-lives, when first twitch response is substantially greater than 10% of baseline, or when a second twitch is present: 0.03 mg/kg by intravenous route
- For reversal of NMBAs with longer half-lives or when first twitch response is close to 10% of baseline: 0.07 mg/kg by intravenous route
- Maximum total dosage is 0.07 mg/kg or up to a total of 5 mg (whichever is less)
- An anticholinergic agent, e.g., atropine sulfate or glycopyrrolate, should be administered prior to or concomitantly with Neostigmine.
The common side effects are-
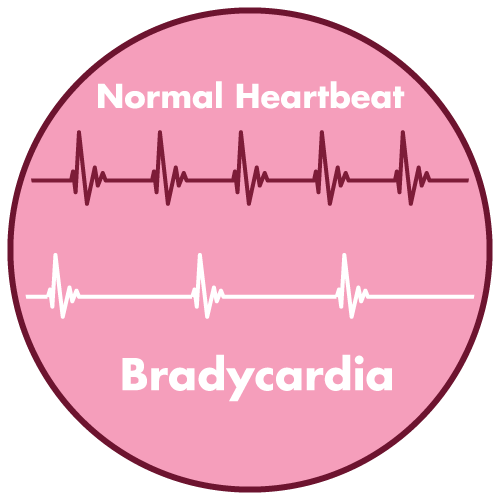
- bradycardia
- hypotension
- tachycardia
- dry mouth
- nausea
- dizziness
- headache
- insomnia
- dyspnea
- pruritus
- Neostigmine has been linked to bradycardia. To reduce the risk of bradycardia, atropine sulfate or glycopyrrolate should be administered prior to Neostigmine.
- In patients with coronary artery disease, cardiac arrhythmias, recent acute coronary syndrome, or myasthenia gravis, Neostigmine should be used with caution. Because of neostigmine methylsulfate's known pharmacology as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, cardiovascular effects such as bradycardia, hypotension, or dysrhythmia would be expected.
- Because of the possibility of hypersensitivity, atropine and anaphylaxis medications should be readily available.
- When neuromuscular blockade is minimal, high doses of Neostigmine can cause neuromuscular dysfunction. If neuromuscular blockade recovery is nearly complete, the dose of Neostigmine should be reduced.
- It is critical to distinguish between myasthenic and cholinergic crises caused by Neostigmine overdosage. Both conditions cause severe muscle weakness but require very different treatments.
Contraindication
Contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to neostigmine.
none known.
Neostigmine is contraindicated in-
- Peritonitis
- mechanical obstruction of the intestinal or urinary tract
 Bangla
Bangla English
English