| Name | Nitroglycerin |
| Classes |
Cardiovascular Agent Vasodilator Antianginal Agent |
| Diseases |
Angina Cardiovascular Disease Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) |
Nitroglycerin
Nitroglycerin is a nitrate that acts as a vasodilator. It works by relaxing smooth muscle in blood vessels, which leads to dilation and increased blood flow.
Nitroglycerin is indicated for the relief of angina pectoris and the prophylaxis of angina attacks.
- At the first sign of an acute anginal attack, one tablet should be dissolved under the tongue or in the buccal pouch. The dose should be repeated every 5 minutes until relief is obtained. If the pain persists after taking three tablets in 15 minutes, or if the pain is different than usual, seek medical attention immediately. Nitroglycerine can be used as a preventative measure 5 to 10 minutes before engaging in activities that could trigger an acute attack.
- The patient should rest during administration, preferably in a sitting position.
- In patients with renal failure, no dosage adjustments are required.
The most common adverse reactions of nitroglycerin include-
- headache
- dizziness
- lightheadedness
- nausea
- hypotension
- flushing
- syncope
- orthostatic hypotension
- The efficacy of sublingual nitroglycerin in patients with acute myocardial infarction or congestive heart failure is uncertain. If nitroglycerin is chosen for use in such cases, careful clinical or hemodynamic monitoring is necessary because hypotension and tachycardia may occur.
- It is advised to use the minimum effective dose to relieve acute angina attacks, as excessive use can result in tolerance.
- Nitroglycerin can cause severe hypotension, especially when standing, even with small doses, so it should be used cautiously in patients who may be hypotensive or have low blood volume.
- Nitroglycerin-induced hypotension may be accompanied by bradycardia and increased angina pectoris.
Contraindication
- Nitroglycerin is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to it.
- Administration of Nitroglycerine is contraindicated in patients who are using a phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) inhibitor (e.g., sildenafil citrate, tadalafil, vardenafil hydrochloride) since these compounds have been shown to potentiate the hypotensive effects of organic nitrates.
None known.
Sublingual nitroglycerin therapy is contraindicated in patients with-
- early myocardial infarction
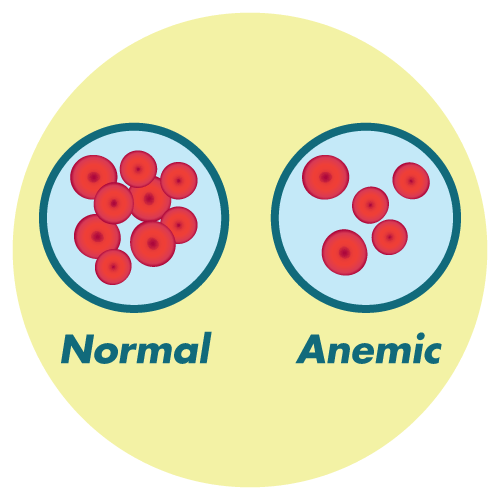
- severe anemia
- increased intracranial pressure
 Bangla
Bangla English
English