| Name | Oxymorphone Hydrochloride |
| Classes |
Analgesic / Pain Killer Central Nervous System Agent Narcotic/Opioid Analgesic |
| Diseases |
Anxiety CNS Disorder Pain |
Oxymorphone Hydrochloride
Oxymorphone Hydrochloride is an opioid agonist that acts centrally to relieve pain. It exerts its analgesic effects by binding to specific receptors in the central nervous system, primarily the mu-opioid receptors. Activation of these receptors modulates the perception of pain and alters the response to pain stimuli.
Oxymorphone Hydrochloride is indicated for the management of moderate to severe pain where the use of an opioid analgesic is appropriate, and alternative treatments are inadequate.
-
Initiation of Therapy for Opioid-Naïve and Non-Tolerant Patients:
- Begin with 5 mg tablets administered orally every 12 hours.
-
Conversion from Another Opioid:
- When switching from another opioid, utilize available conversion factors to estimate the appropriate dose for Oxymorphone Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets.
-
Dose Adjustment and Titration:
- Adjust the dose at intervals of 3 to 7 days.
- Increase the dosage in increments of 5 to 10 mg every 12 hours (equivalent to 10 to 20 mg per day).
-
Administration Instructions:
- Administer the tablets on an empty stomach, at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal.
- Take each Oxymorphone Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablet one at a time, ensuring complete swallowing with an adequate amount of water immediately after placing it in the mouth.
-
Discontinuation in Physically Dependent Patients:
- Avoid abrupt discontinuation of Oxymorphone Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets in physically dependent patients.
-
Swallowing Instructions:
- Instruct patients to swallow Oxymorphone Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets intact.
- Dose Adjustment for Hepatic and Renal Impairment:
- Reduce the dose of Oxymorphone Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets in patients with mild hepatic impairment and those with renal impairment.
Common adverse reactions associated with Oxymorphone Hydrochloride may include:
- Constipation
- Nausea
- Somnolence
- Dizziness
- Vomiting
- Pruritus
- Headache
- Dry mouth
- Sweating
-
Interaction with CNS Depressants:
- Concomitant use with other central nervous system (CNS) depressants may lead to profound sedation, respiratory depression, and potential fatal outcomes.
- Consider dose reduction for either or both drugs due to additive pharmacological effects.
-
Elderly, Cachectic, and Debilitated Patients, and Those with Chronic Pulmonary Disease:
- Monitor this patient population closely due to an elevated risk of life-threatening respiratory depression.
- Exercise caution and vigilance in managing these patients.
-
Hypotensive Effect:
- Monitor patients for hypotensive effects during the initiation and titration of the dosage.
-
Patients with Head Injury or Increased Intracranial Pressure:
- Monitor patients with head injury or heightened intracranial pressure for sedation and respiratory depression.
- Avoid the use of Oxymorphone Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets in patients with impaired consciousness or those in a coma susceptible to intracranial effects related to CO2 retention.
-
Difficulty in Swallowing or Underlying GI Disorders:
- Exercise caution when using Oxymorphone Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets in patients who have difficulty swallowing or possess underlying gastrointestinal disorders that may predispose them to obstruction.
Contraindication
Contraindicated in patient with hypersensitivity to oxymorphone.
None known.
Oxymorphone is contraindicated in patients with the following conditions-
- Significant respiratory depression
- Acute or severe bronchial asthma
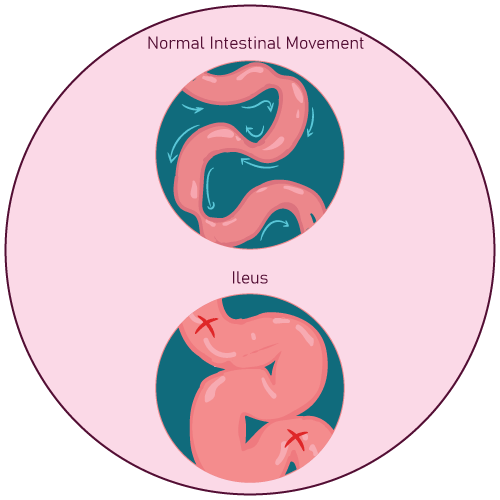
- Known or suspected paralytic ileus and gastrointestinal obstruction
- Moderate or severe hepatic impairment
 Bangla
Bangla English
English