| Name | Phenoxymethyl Penicillin |
| Classes |
Antiinfective Agent Antibiotic Penicillin |
| Diseases |
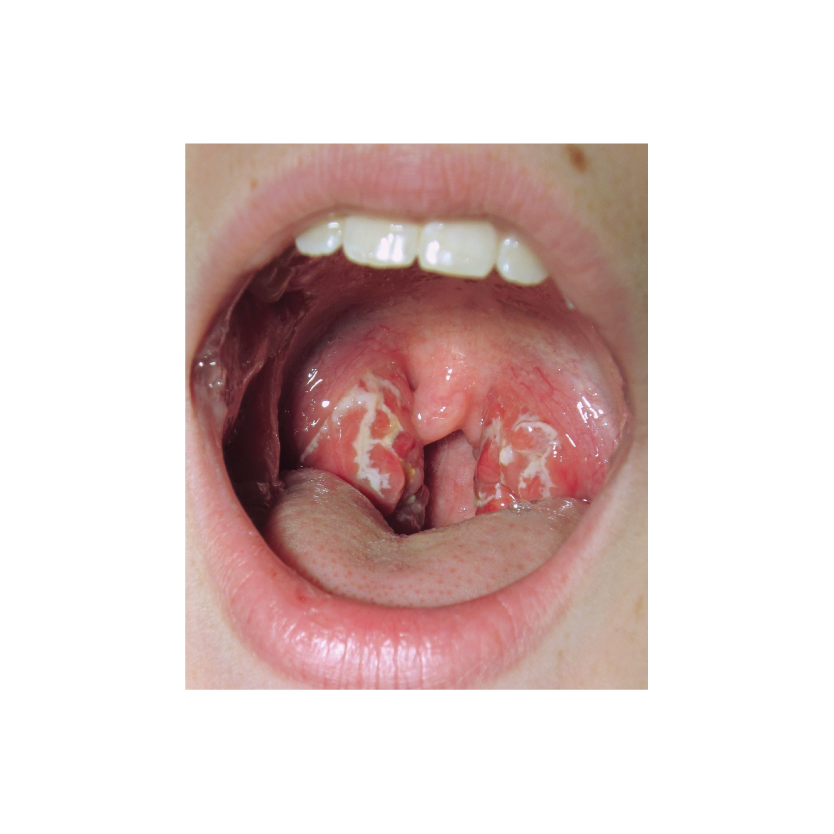
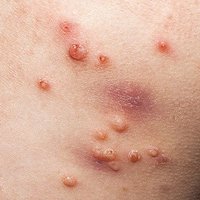
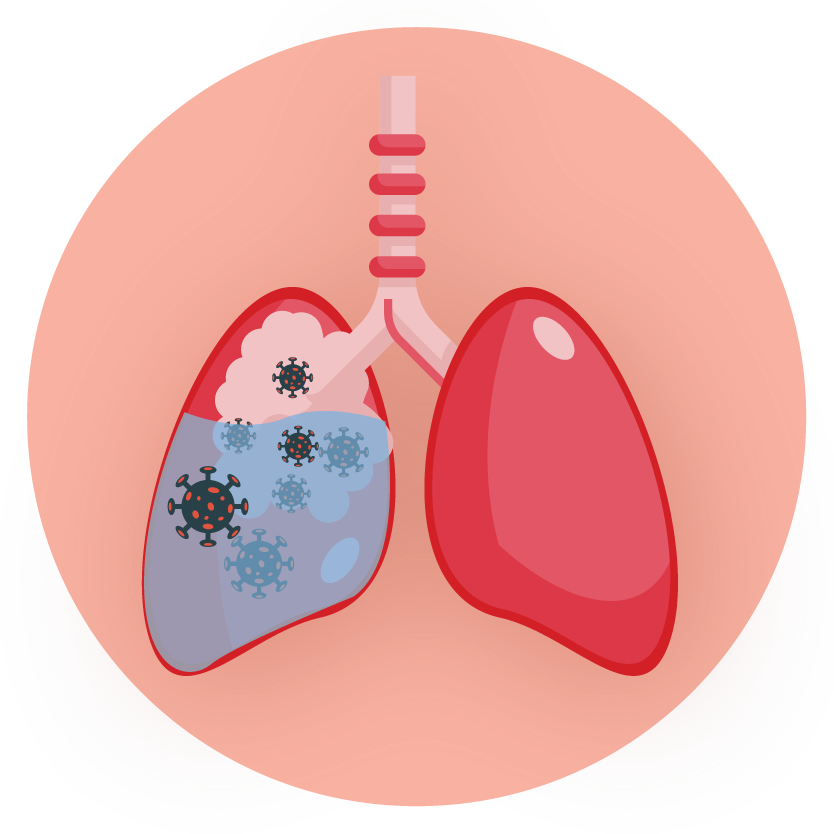
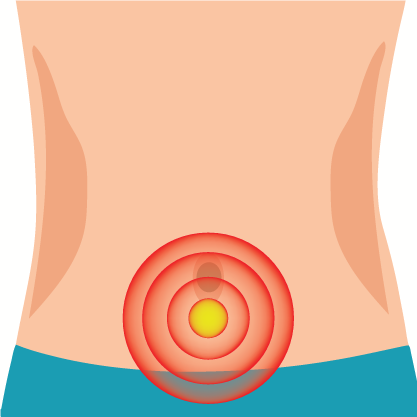
Cellulitis Chest Infection Dental Abscess Infectious Disease Otitis Tonsillitis |
Phenoxymethyl Penicillin
Phenoxymethyl Penicillin or penicillin v is a beta lactam antibiotic that kills bacteria by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. It is not hydrolyzed by stomach acid therefore it is orally available.
Phenoxymethyl Penicillin is indicated for the following streptococcal infection-
- Pharyngitis
- Scarlet fever
- Skin and soft tissue infections (e.g erysipelas)
Pneumococcal infections-
- Pneumonia
- Otitis media
- Vincent's gingivitis and pharyngitis
- Phenoxymethylpenicillin dosage and frequency are determined by the severity and location of the illness, as well as the microorganisms to be expected.
- Phenoxymethylpenicillin Solution should be taken at least 30 minutes before or 2 hours after eating, as the drug's absorption is significantly reduced when taken with food.
- 250mg of phenoxymethylpenicillin is roughly equivalent to 400,000 units.
Adults and children over 12 years: 250mg - 500mg every six hours
Children: Infants (up to 1 year): 62.5mg every 6 hours
1-5 years: 125mg every six hours
6-12 years: 250mg every six hours
Renal impairment: If renal function is severely affected, the dosage should be adjusted.
Hepatic dysfunction: When individuals have both compromised liver function and renal failure, dosage adjustments may be indicated. The liver could be a main excretion route in this case.
Renal impairment: If renal function is severely affected, the dosage should be adjusted.
Hepatic dysfunction: When individuals have both compromised liver function and renal failure, dosage adjustments may be indicated. The liver could be a main excretion route in this case.
Side effects associated with the use of phenoxymethyl penicillin are-
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Urticaria
- Rash
- Penicillin should be taken with caution in people who have a history of severe allergies or asthma.
- In patients with severe sickness, nausea, vomiting, gastric dilatation, cardiospasm, or intestinal hypermotility, the oral route of administration should be avoided.
- Antibiotic use for an extended period of time may increase the growth of non-susceptible organisms, such as fungus. If superinfection occurs, the necessary precautions should be taken.
Contraindication
Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to penicillin or other beta lactam antibiotics-
 Bangla
Bangla English
English