| Name | Progesterone |
| Classes |
Hormonal Agent Sex Hormone Steroid |
| Diseases |
Amenorrhea Genito-Urinary Disease Uterine Bleeding |
Progesterone
Progesterone is a hormone that is naturally produced in the body by the corpus luteum of the ovary and the placenta during pregnancy. It plays a crucial role in the menstrual cycle, preparing the uterus for pregnancy and helping to maintain a healthy pregnancy.
The mechanism of action of progesterone is primarily mediated by its binding to progesterone receptors (PRs), which are present in a variety of tissues, including the uterus, breast, brain, and bone. Once progesterone binds to the PRs, it triggers a cascade of cellular events that ultimately lead to changes in gene expression and cellular activity.
Progesterone is a hormone medication used to treat a variety of conditions, including-
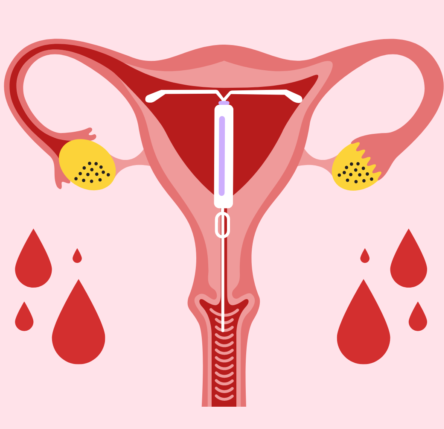
- secondary amenorrhea (absence of menstrual periods)
- abnormal uterine bleeding, premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
- infertility
- endometriosis
- part of hormone replacement therapy in menopausal women. It is also used in assisted reproductive technology (ART) to support pregnancy
- Prevention of Endometrial Hyperplasia/ Endometriosis: Progesterone Capsules should be given as a single daily dose at bedtime, 200 mg orally for 12 days sequentially per 28-day cycle, to a postmenopausal woman with a uterus who is receiving daily conjugated estrogens tablets.
- Treatment of Secondary Amenorrhea: Progesterone Capsules may be given as a single daily dose of 400 mg at bedtime for 10 days.
- Abnormal uterine bleeding: 5-10 mg daily for 5-10 days
- Premenstrual syndrome (PMS): 200 mg daily for 14 days
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) in menopausal women: 200 mg daily for 12-14 days of a 28-day cycle
- Infertility: 50 mg to 400 mg daily for up to 10 days after ovulation.
Progesterone capsules can cause several side effects, including:
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Headache
- Nausea
- Breast tenderness
- Mood changes, such as depression or anxiety
- Irritability
- Fatigue
- Hot flashes
- Abdominal cramps or bloating
- Vaginal discharge or itching
- Changes in menstrual periods
- Acne
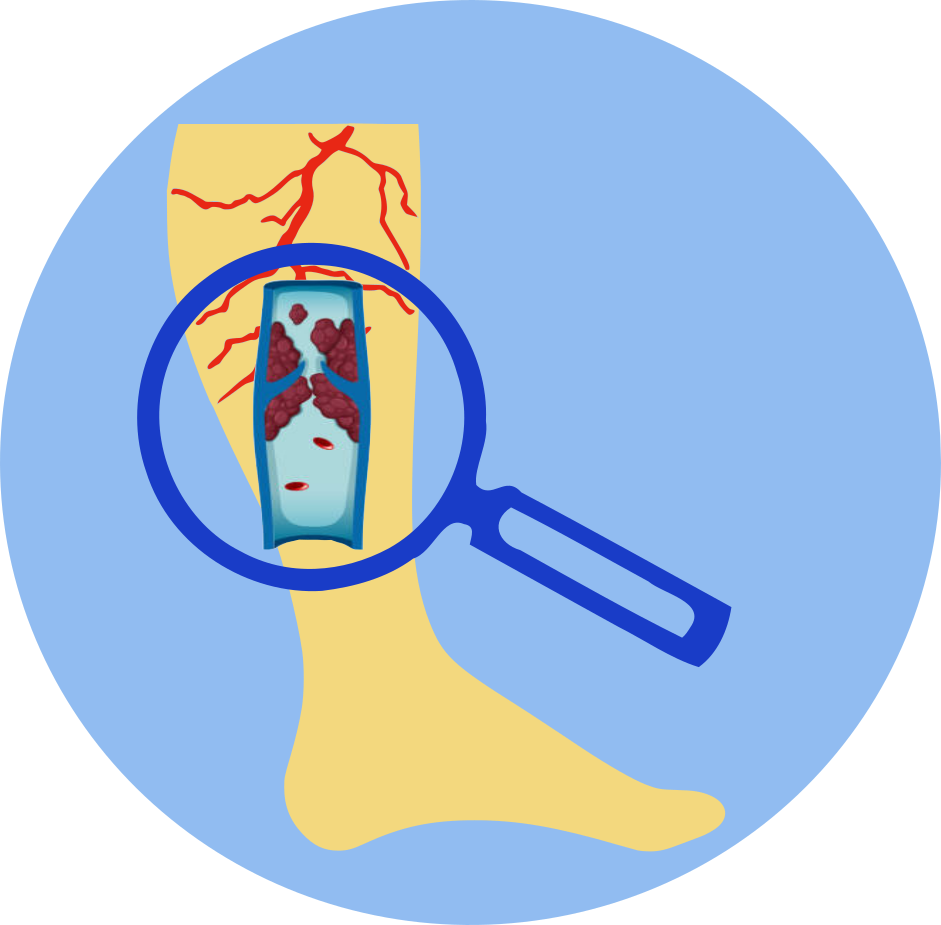
- The estrogen plus progestin substudy of the Women's Health Initiative (WHI) discovered that postmenopausal women (aged 50 to 79 years) taking daily oral conjugated estrogens (CE) [0.625 mg] combined with medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) [2.5 mg] for 5.6 years had a higher risk of deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, stroke, and myocardial infarction than those taking a placebo.
- Estrogens plus progestin therapy should not be utilized for preventing cardiovascular disease or dementia. Additionally, the WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy revealed a greater risk of invasive breast cancer.
- Progestins combined with estrogens should be prescribed in the lowest effective dosages and for the shortest duration possible, based on treatment goals and individual risks. Studies have shown that adding progestin for 10 or more days of a cycle of estrogen administration or every day with estrogen in a continuous regimen can lower the incidence of endometrial hyperplasia. Endometrial hyperplasia may precede endometrial cancer.
- Progesterone can cause fluid retention, so women with cardiac or renal problems should be closely monitored.
- Progesterone capsules may cause momentary dizziness and drowsiness and should be used carefully when driving or operating machinery. Progesterone capsules should be taken once per day at bedtime.
Contraindication
Progesterone Capsules should not be used in patients with known hypersensitivity to its ingredients.
Progesterone Capsules contain peanut oil and should never be used by patients allergic to peanuts.
Progesterone is contraindicated in the following conditions-
- Undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding.
- Known, suspected, or history of breast cancer.
- Active deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism or history of these conditions.
- Active arterial thromboembolic disease (for example, stroke and myocardial infarction), or a history of these conditions.
- Known liver dysfunction or disease.
- Known or suspected pregnancy.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English