| Name | Protamin Sulphate |
| Classes |
Coagulation Modifier Haematological Agent Antiplatelet Agent |
| Diseases |
Heparin Overdose Toxicity |
Protamin Sulphate
Protamine sulfate is a cationic protein that binds with high affinity to heparin, neutralizing its anticoagulant activity by forming a stable complex.
- Protamine sulfate is indicated for the complete or partial reversal of the anticoagulant effect of heparin in the setting of heparin overdose or when the use of heparin needs to be immediately reversed.
- It can also be used to reverse the anticoagulant effect of low molecular weight heparin (LMWH), although the dose and timing of protamine sulfate administration may differ from those used for heparin.
- The dose of protamine sulfate required to reverse heparin anticoagulation is dependent on the amount of heparin administered and the timing of protamine administration. The dose of protamine should be based on the amount of heparin remaining in the patient's circulation, not the total dose administered.
- In general, a dose of 1 mg of protamine sulfate per 100 units of heparin is recommended, administered by slow intravenous injection over 10 minutes. If the initial dose does not achieve the desired level of anticoagulation reversal, additional doses can be administered.
- The maximum recommended dose of protamine sulfate is 50 mg in a single administration, and no more than 5 mg/minute should be given to avoid hypotension.
Side effects reported with the use of protamine sulphate include-
- Hypotension
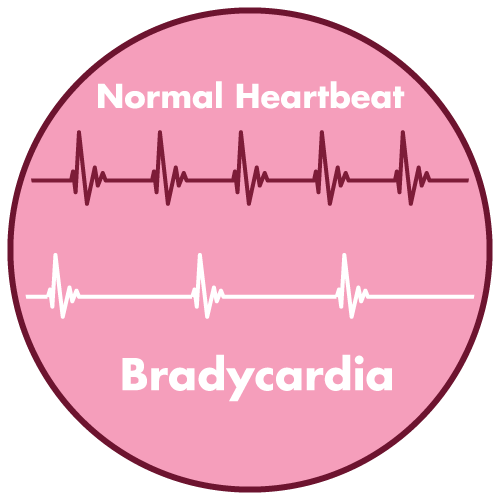
- Bradycardia
- Flushing
- Dyspnea
- Nausea/vomiting
- Transient taste disturbance
- Allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis
- Protamine sulfate should be used with caution in patients with a known hypersensitivity to fish or fish products, as it is derived from salmon sperm.
- Protamine sulfate can cause hypotension, particularly if administered rapidly or in high doses. Blood pressure should be closely monitored during and after administration.
- Protamine sulfate can cause bradycardia, particularly in patients receiving beta-blockers. Heart rate should be closely monitored during and after administration.
- Protamine sulfate can cause an allergic reaction, ranging from mild to severe (including anaphylaxis), even in patients with no known previous exposure. Patients should be monitored closely for signs of allergic reaction during and after administration.
- The safety and efficacy of protamine sulfate have not been established in pediatric patients, pregnant women, or nursing mothers.
Contraindication
Protamine sulfate is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to the drug or any of its components.
None known.
None known.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English