| Name | Pyridostigmine |
| Classes |
Central Nervous System Agent Cholinergic Agent Muscle Stimulant |
| Diseases |
Myasthenia Gravis Neuromascular Disorder |
Pyridostigmine
Pyridostigmine is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Acetylcholinesterase is the enzyme responsible for breaking down acetylcholine. Therefore, by blocking the enzyme, pyridostigmine increases the acetylcholine concentration in the synaptic cleft or neuro-muscular junction.
Pyridostigmine is indicated for the treatment of-
- Myasthenia gravis
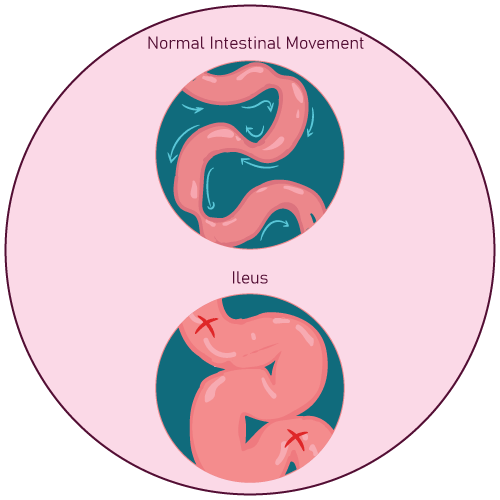
- paralytic ileus
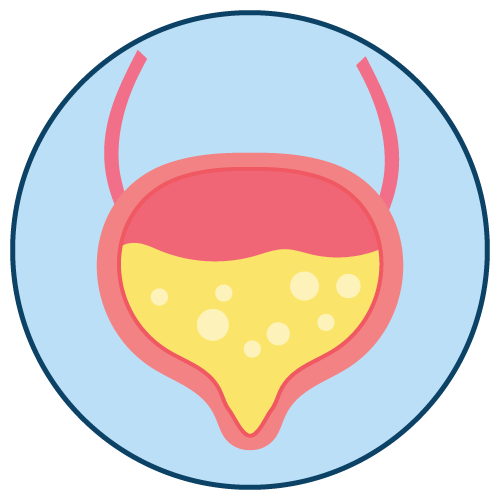
- post-operative urinary retention
Myasthenia gravis
- Adults: When maximum strength is required, doses of 30 to 120mg are administered at regular intervals throughout the day (for example, on rising and before mealtimes). A dose's usual duration of action is 3 to 4 hours during the day, but a longer effect (6 hours) is often obtained with a dose taken before retiring to bed. The total daily dose is usually between 5 and 20 tablets, but some patients may require higher doses.
- Paediatric population: Children under the age of six should start with half a Mestinon tablet (30mg), while children aged six to twelve should start with one tablet (60mg). Dosage should be gradually increased in 15-30mg increments daily until maximum improvement is obtained. Total daily requirements are usually in the range to 30 – 360mg.
Paralytic ileus, post-operative urinary retention
- Adults: The usual dose is 1 to 4 tablets (60 – 240mg) per day.
- Paediatric population: The usual dose is 15 – 60mg per day.
The frequency of these doses may be varied according to the needs of the patient.
The common side effects are-
- nausea
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- abdominal cramps
- increased peristalsis
- increased bronchial secretion
- salivation
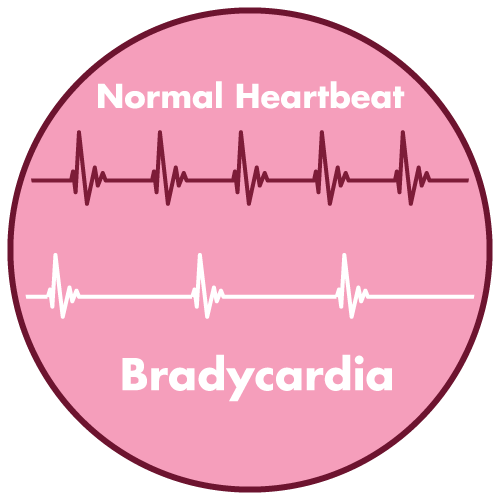
- bradycardia
- miosis
- Extreme caution is required when administering Pyridostigmine to patients with obstructive respiratory diseases like bronchial asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Care should also be taken in patients with:
-
- Arrhythmias such as bradycardia and AV block(elderly patients may be more susceptible to dysrhythmias than the young adult)
- Recent coronary occlusion
- Hypotension,
- Vagotonia
- Peptic ulcer
- Epilepsy or Parkinsonism
- Hyperthyroidism
-
When relatively high doses of Pyridostigmine are administered to myasthenic patients, atropine or other anticholinergic drugs may be required to counteract the muscarinic effects. It should be noted that the slower gastro-intestinal motility caused by these medications may interfere with Pyridostigmine absorption.
- The possibility of "cholinergic crisis" due to Pyridostigmine overdosage, and its distinction from "myasthenic crisis" due to increased disease severity, must be considered in all patients. Both types of crises are characterized by increased muscle weakness; however, whereas myasthenic crisis may necessitate more intensive anticholinesterase treatment, cholinergic crisis necessitates the immediate discontinuation of this treatment and the implementation of appropriate supportive measures, including respiratory assistance.
-
Pyridostigmine requirements are typically significantly reduced following thymectomy or when additional therapy (steroids, immunosuppressive drugs) is administered.
- Patients with rare hereditary galactose intolerance, Lapp lactase deficiency, or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not use this medication.
Contraindication
Pyridostigmine is contraindicated in patients with Hypersensitivity to the active substance, bromides or to any of the excipients.
None known.
Contraindicated in Mechanical gastro-intestinal or urinary obstruction.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English