| Name | Flutamide |
| Classes |
Anticancer/Antineoplastic Agent Hormonal Agent Antiandrogen Hormone |
| Diseases |
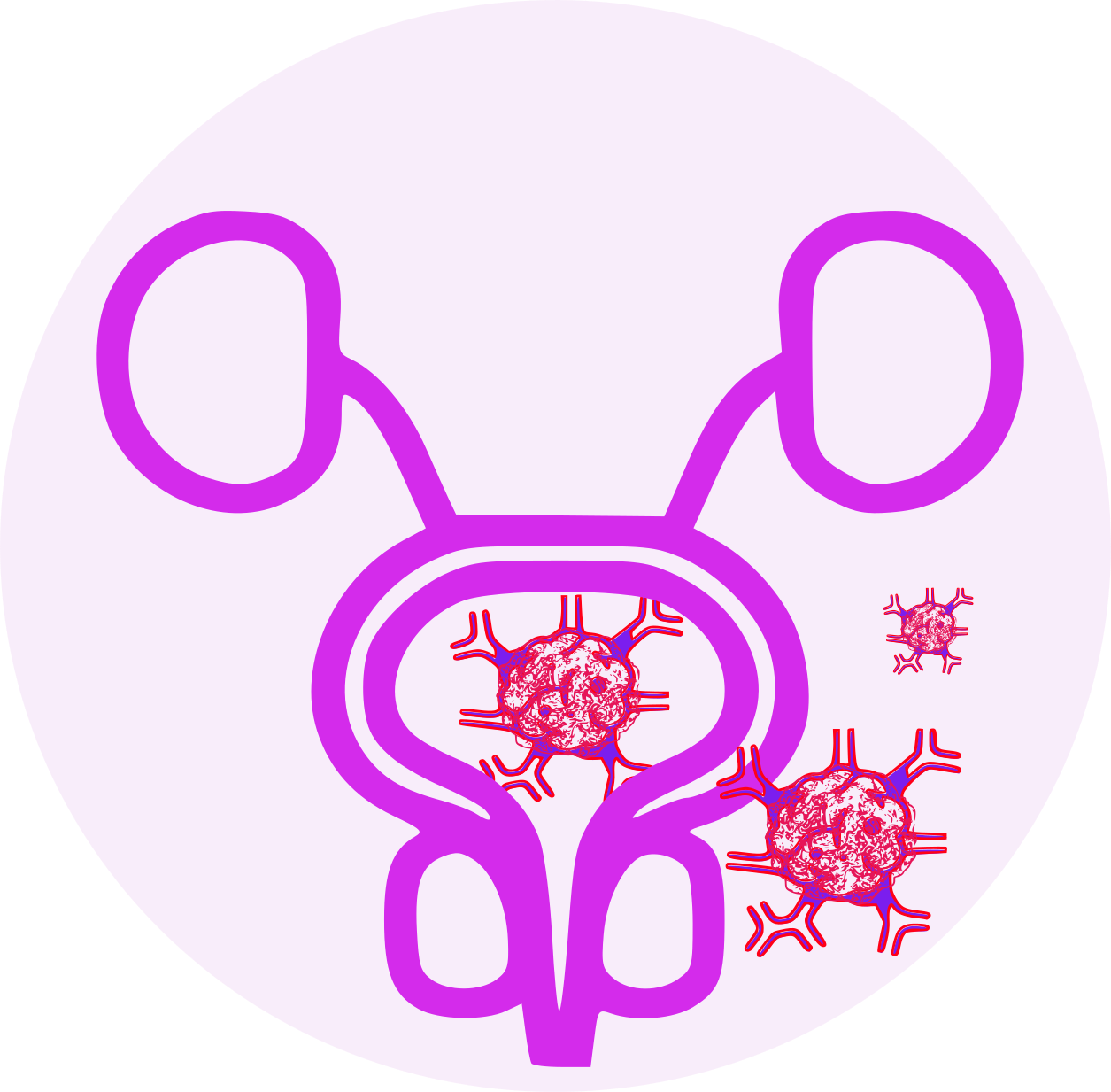
Cancer Prostate Cancer |
Flutamide
Flutamide is a nonsteroidal orally active antiandrogen drug. It exerts its antiandrogenic action by inhibiting androgen uptake and/or by inhibiting nuclear binding of androgen in target tissues or both. Prostatic carcinoma is known to be androgen-sensitive and responds to treatment that counteracts the effect of androgen and/or removes the source of androgen, e.g., castration.
Flutamide capsules are indicated for use in combination with LHRH-agonists for-
- Stage B2 -C Prostatic Carcinoma
- Stage D2 Metastatic Carcinoma
The recommended dosage is 2 capsules 3 times a day at 8 hour intervals for a total daily dose of 750 mg.
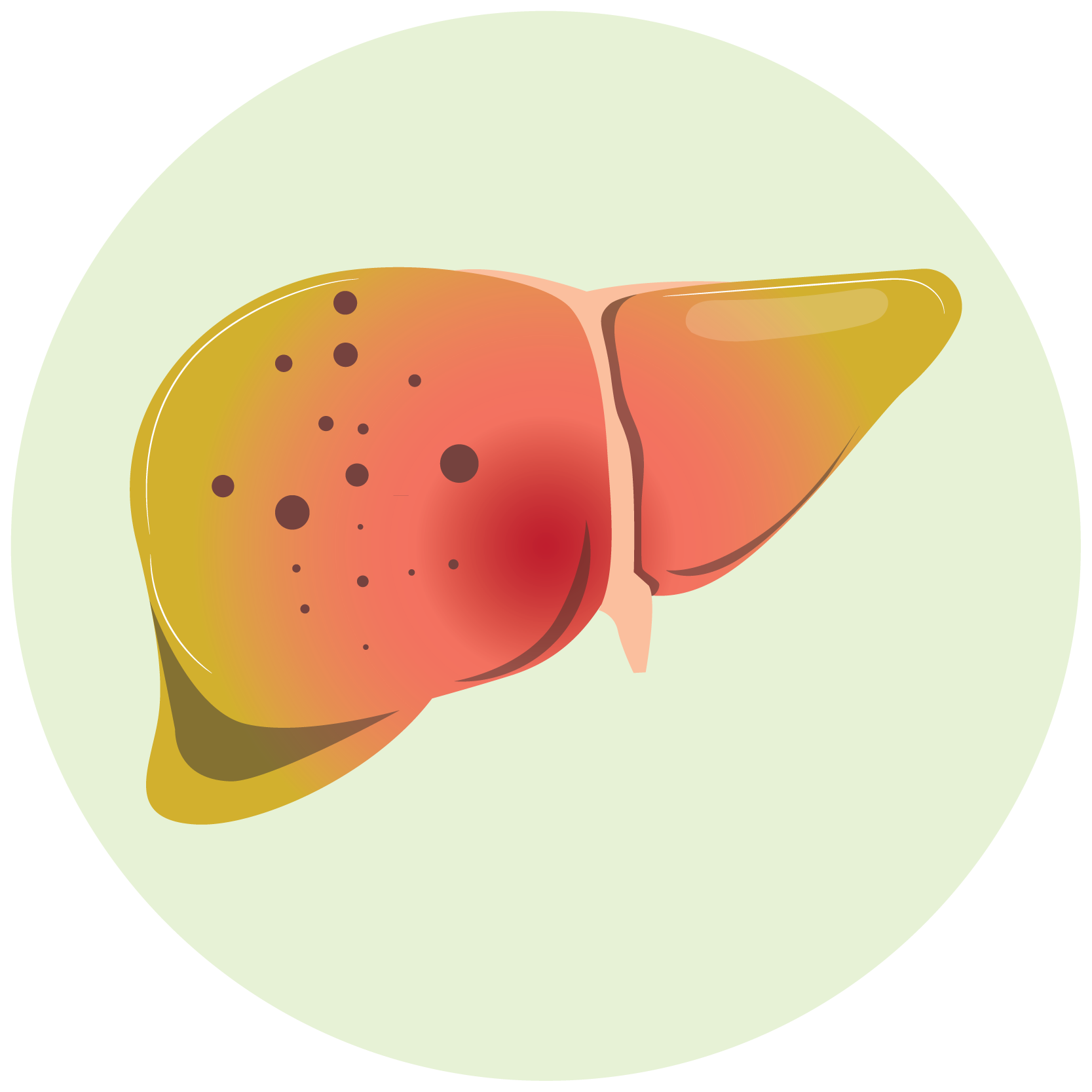
- Hepatic Injury: There have been postmarketing reports of flutamide patients being hospitalized and, in rare cases, dying from liver failure. Elevated serum transaminase levels, jaundice, hepatic encephalopathy, and death from acute hepatic failure were all signs of hepatic injury. In some patients, the hepatic injury was reversible after therapy was stopped. Approximately half of the reported cases occurred within the first three months of flutamide treatment.
- Before beginning flutamide treatment, serum transaminase levels should be measured. Flutamide is not recommended for patients with ALT levels that are more than twice the upper limit of normal. Serum transaminase levels should then be measured monthly for the first four months of therapy, and then on a regular basis after that.
- Flutamide capsules are only for men. This product has no indication for use in women and should not be used in this population, especially for non-serious or non-life threatening conditions.
- Flutamide can harm a fetus if given to a pregnant woman.
- 4-nitro-3-fluoro-methylaniline is a flutamide metabolite. Flutamide administration resulted in several toxicities consistent with aniline exposure, including methemoglobinemia, hemolytic anemia, and cholestatic jaundice in both animals and humans. Patients who are susceptible to aniline toxicity (e.g., those with glucose-6-phosphate.
- Gynecomastia occurred in 9% of patients receiving flutamide along with medical castration in clinical trials.
Contraindication
Flutamide capsules are contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to flutamide or any component of this preparation.
None known.
Flutamide capsules are contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment (baseline hepatic enzymes should be evaluated prior to treatment).
 Bangla
Bangla English
English