| Name | Labetalol Hydrochloride |
| Classes |
Cardiovascular Agent Antihypertensive Beta-Adrenoceptor Blocker |
| Diseases |
Cardiovascular Disease Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) |
Labetalol Hydrochloride
Labetalol is a non selective beta blocker. It is also functions as alpha agonist.
Hypertension and angina:
Starting with 100mg twice a day, the treatment should be gradually increased. This may be sufficient to manage blood pressure in people who are currently taking antihypertensives and who have a low body weight. Increases in dose of 100mg twice daily should be made every two weeks in others. Many patients' blood pressure can be stabilized with 200mg twice daily, and up to 800mg twice daily may be provided. Daily dosages of up to 2400mg have been given to patients with severe, resistant hypertension. These doses should be divided into three or four daily doses.
Commonly associated side effects include-
- dizziness
- headache
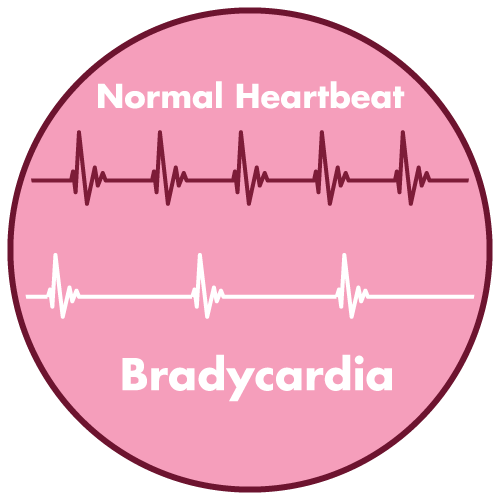
- bradycardia
- orthostatic hypotension (occasionally with syncope)
- dyspnea
- nausea
- abdominal pain
- Asthenia
Impaired Hepatic Function: Labetalol Tablets should be used with caution in patients with impaired hepatic function since metabolism of the drug may be diminished.
Dosing with Labetalol Tablets should not be interrupted or discontinued without a physician's advice.
Intraoperative Floppy Iris Syndrome (IFIS) has been observed during cataract surgery in some patients treated with alpha-1 blockers (labetalol is an alpha/beta blocker).
Contraindication
Labetalol is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any component of the product and other drugs belonging to the beta blocker class, such as-
Labetalol is contraindicated in
- bronchial asthma
- overt cardiac failure
- greater-than-first-degree heart block
- cardiogenic shock
- severe bradycardia
- other conditions associated with severe and prolonged hypotension
 Bangla
Bangla English
English