| Name | Sulfinpyrazone |
| Classes |
Metabolic Agent Antigout Agent |
| Diseases |
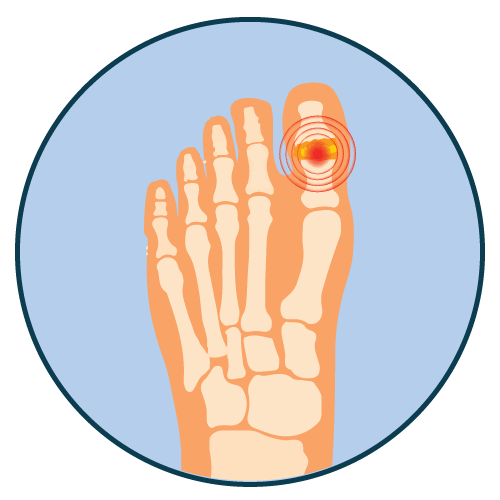
Arthritis Gout Hyperuricemia Inflammatory Disease |
Sulfinpyrazone
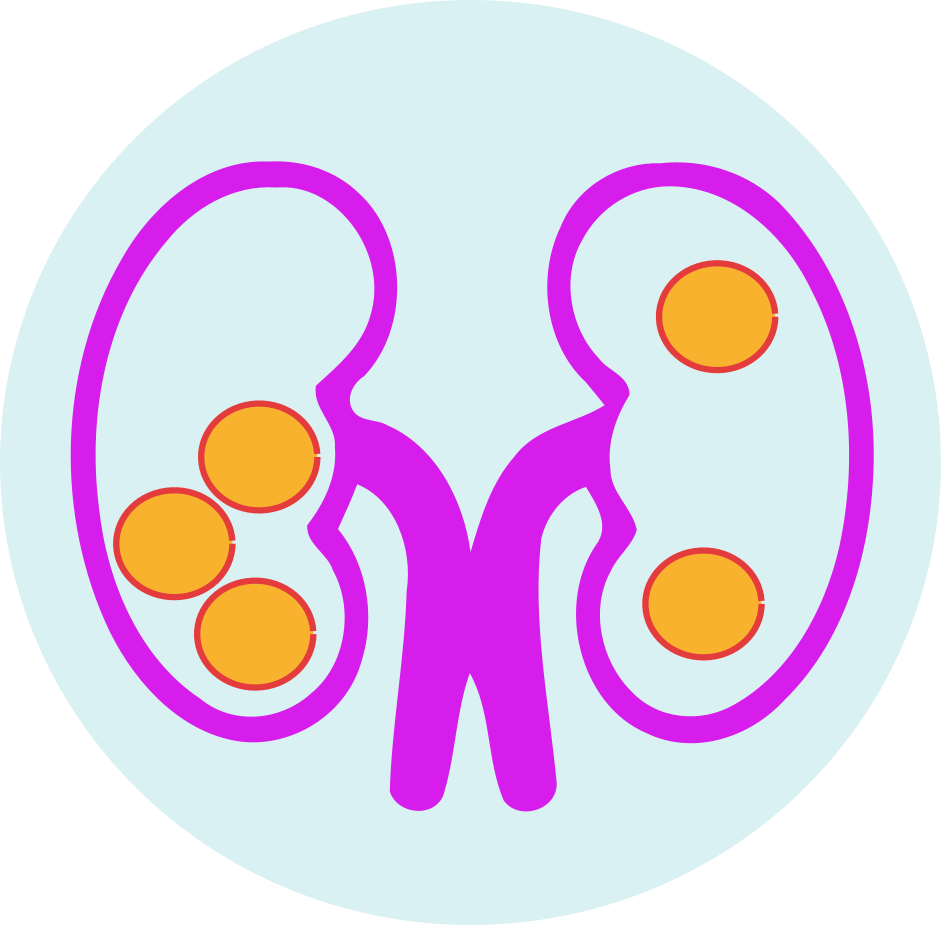
The mechanism of action of Sulfinpyrazone is not entirely understood, but it is believed to work by inhibiting the action of an enzyme called xanthine oxidase, which is responsible for the conversion of xanthine to uric acid. By inhibiting the action of xanthine oxidase, Sulfinpyrazone reduces the amount of uric acid produced and increases the excretion of uric acid by the kidneys. This helps to prevent the formation of gout and kidney stones caused by high levels of uric acid in the blood.
Sulfapyrazone is indicated in prevention of gout and kidney stones caused by high levels of uric acid in the blood.
- The usual starting dose is 200 mg twice daily, taken with meals.
- The dosage can be increased up to 800 mg daily in divided doses, as needed.
- It should be used with caution in patients with kidney or liver dysfunction.
Common side effects may include-
- nausea
- diarrhea
- stomach pain
- headache
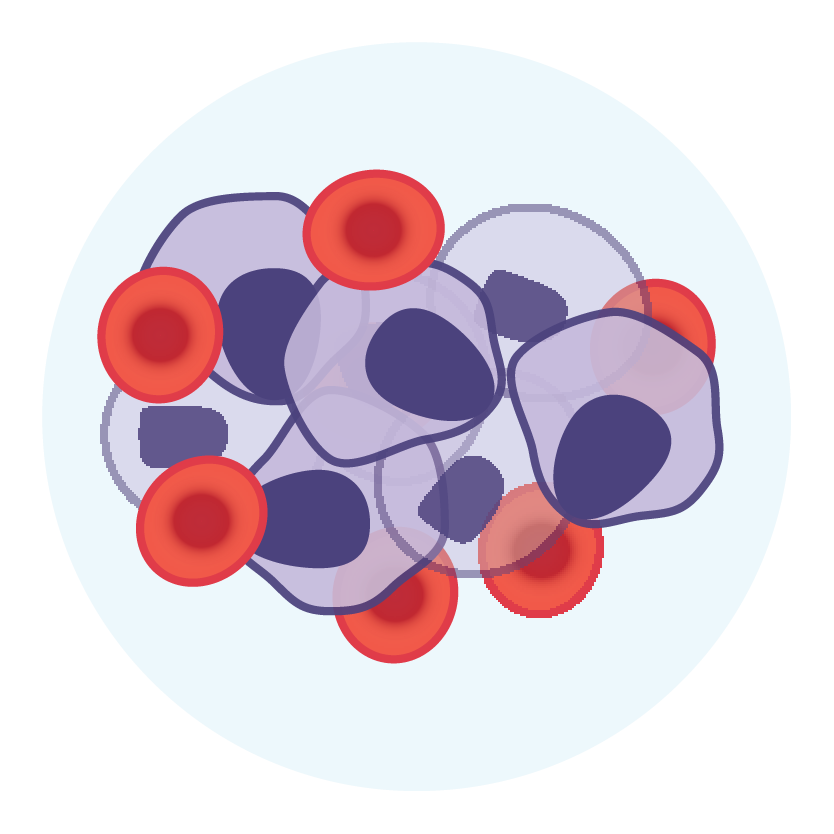
- blood disorders
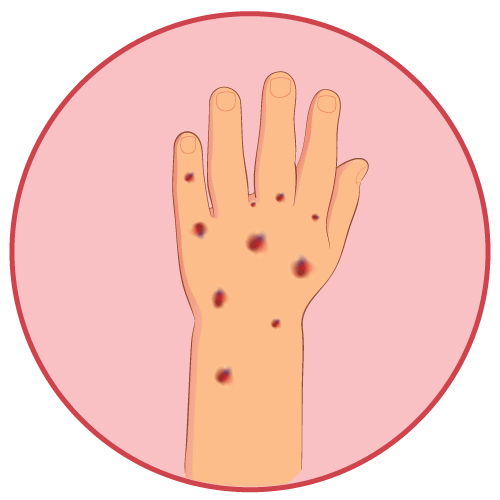
- bleeding
- stomach or intestinal ulcers
- Sulfinpyrazone may increase the risk of bleeding in patients taking anticoagulants or other blood-thinning medications.
- It may also cause blood disorders, such as agranulocytosis, hemolytic anemia, or thrombocytopenia.
- Sulfinpyrazone may cause stomach or intestinal ulcers or bleeding.
- Patients should be monitored for signs of blood disorders or bleeding.
Contraindication
It should not be used in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to sulfonamides such as-
None known.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English