| Name | Nifedipine |
| Classes |
Cardiovascular Agent Antihypertensive Calcium Channel Blocker |
| Diseases |
Angina Cardiovascular Disease Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) |
Nifedipine
Nifedipine is a calcium channel blocker that belongs to the dihydropyridine class. It works by relaxing and opening blood arteries, allowing blood to circulate more freely throughout the body. This helps the heart to perform more efficiently by lowering blood pressure.
Nifedipine is indicated for the treatment of-
- Hypertension
- Prophylaxis of chronic stable angina pectoris
- The suggested starting dose for mild to severe hypertension is one 20mg tablet once daily. The suggested starting dose for severe hypertension is one 30mg tablet once daily. If necessary, the dosage can be increased to a maximum of 90mg once daily, depending on the individual's needs.
- The suggested first dose for angina pectoris prevention is one 30mg tablet once daily. Individual needs can be met by increasing the dosage up to a maximum of 90mg once daily.
Side effects associated with the use of nifedipine include-
- Headache
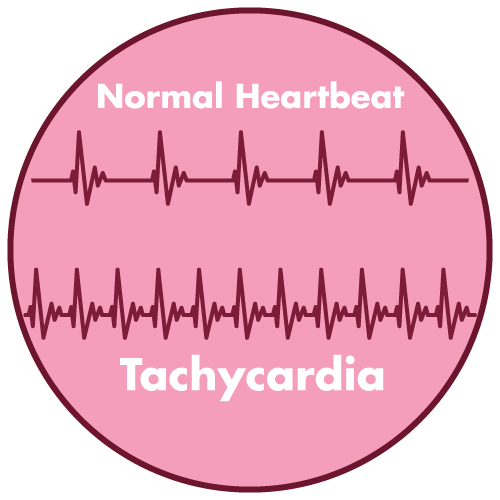
- Tachycardia
- Palpitations
- Flushing
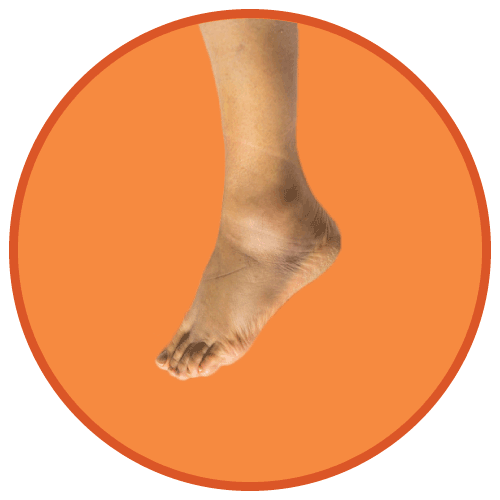
- Peripheral edema
- Dizziness
- Hypotension
- Polyuria
- Asthenia
- Patients with hypotension should be treated with caution since there is a danger of further blood pressure loss, and patients with extremely low blood pressure should be treated with caution.
- Nifedipine should not be taken during pregnancy unless the woman's clinical condition necessitates its use.
- Because nifedipine has been documented to be excreted in human milk and the effects of nifedipine exposure on the newborn are unknown, it is not recommended for use while breastfeeding.
- Patients with hepatic impairment: Careful monitoring and, in severe circumstances, a dose decrease may be required in individuals with compromised liver function.
- The cytochrome P450 3A4 system is responsible for nifedipine metabolism. Drugs that are known to inhibit or promote this enzyme system may thereby affect nifedipine clearance.
- When discontinuing a beta-blocker it is important to taper its dose, if possible, rather than stopping abruptly before beginning nifedipine
Contraindication
- Nifedipine is contraindicated in patients hypersensitivity of nifedipine or other dihydropyridine analogues, such as-
Nifedipine is contraindicated in the following health conditions-
- Cardiogenic shock
- advanced aortic stenosis
- nursing mothers
- GI obstruction
- inflammatory bowel disease
- hypotension
 Bangla
Bangla English
English